Rapid discrimination of the phenotypic variants of von Willebrand disease
- PMID: 26917779
- PMCID: PMC4874227
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2015-11-664680
Rapid discrimination of the phenotypic variants of von Willebrand disease
Abstract
Approximately 20% to 25% of patients with von Willebrand disease (VWD) have a qualitative defect of the von Willebrand factor (VWF) protein activities. Variant VWD typically is classified as type 1C, 2A, 2B, 2M, or 2N depending on the VWF activity defect. Traditionally, diagnosis has relied on multiple clinical laboratory assays to assign VWD phenotype. We developed an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) to measure the various activities of VWF on a single plate and evaluated 160 patient samples enrolled in the Zimmerman Program for the Molecular and Clinical Biology of von Willebrand Disease with type 2 VWD. Using linear discriminate analysis (LDA), this assay was able to identify type 1C, 2A, 2B, 2M, or 2N VWD with an overall accuracy of 92.5% in the patient study cohort. LDA jackknife analysis, a statistical resampling technique, identified variant VWD with an overall accuracy of 88.1%, which predicts the assay's performance in the general population. In addition, this assay demonstrated correlation with traditional clinical laboratory VWF assays. The VWF multiplex activity assay may be useful as a same-day screening assay when considering the diagnosis of variant VWD in an individual patient.
© 2016 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures

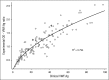
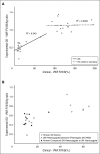
Comment in
-
VWD diagnosis: improved.Blood. 2016 May 19;127(20):2372-3. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-03-703231. Blood. 2016. PMID: 27207322 No abstract available.
References
-
- Nichols WL, Hultin MB, James AH, et al. von Willebrand disease (VWD): evidence-based diagnosis and management guidelines, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) Expert Panel report (USA). Haemophilia. 2008;14(2):171–232. - PubMed
-
- Rodeghiero F, Castaman G, Dini E. Epidemiological investigation of the prevalence of von Willebrand’s disease. Blood. 1987;69(2):454–459. - PubMed
-
- Werner EJ, Broxson EH, Tucker EL, Giroux DS, Shults J, Abshire TC. Prevalence of von Willebrand disease in children: a multiethnic study. J Pediatr. 1993;123(6):893–898. - PubMed
-
- Werner EJ, Abshire TC, Giroux DS, Tucker EL, Broxson EH. Relative value of diagnostic studies for von Willebrand disease. J Pediatr. 1992;121(1):34–38. - PubMed
-
- Castaman G, Eikenboom JC, Bertina RM, Rodeghiero F. Inconsistency of association between type 1 von Willebrand disease phenotype and genotype in families identified in an epidemiological investigation. Thromb Haemost. 1999;82(3):1065–1070. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

