Electrographic status epilepticus in sleep in an adult with cerebral folate deficiency
- PMID: 26918205
- PMCID: PMC4753830
- DOI: 10.1212/CPJ.0000000000000199
Electrographic status epilepticus in sleep in an adult with cerebral folate deficiency
Figures

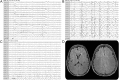
References
-
- Serrano M, Perez-Duenas B, Montoya J, Ormazabal A, Artuch R. Genetic causes of cerebral folate deficiency: clinical, biochemical and therapeutic aspects. Drug Discov Today 2012;17:1299–1306. - PubMed
-
- Ramaekers VT, Rothenberg SP, Sequeira JM, et al. Autoantibodies to folate receptors in the cerebral folate deficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med 2005;352:1985–1991. - PubMed
-
- Sánchez Fernández I, Loddenkemper T, Peters JM, Kothare SV. Electrical status epilepticus in sleep: clinical presentation and pathophysiology. Pediatr Neurol 2012;47:390–410. - PubMed
-
- Mariotti P, Della MG, Iuvone L, et al. Is ESES/CSWS a strictly age-related disorder? Clin Neurophysiol 2000;111:452–456. - PubMed
-
- Lucey BP, Duntley SP. Electrical status epilepticus during sleep in an adult. Sleep Med 2008;9:332–334. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
