Urinary Biomarkers Indicative of Apoptosis and Acute Kidney Injury in the Critically Ill
- PMID: 26918334
- PMCID: PMC4769222
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149956
Urinary Biomarkers Indicative of Apoptosis and Acute Kidney Injury in the Critically Ill
Abstract
Background: Apoptosis is a key mechanism involved in ischemic acute kidney injury (AKI), but its role in septic AKI is controversial. Biomarkers indicative of apoptosis could potentially detect developing AKI prior to its clinical diagnosis.
Methods: As a part of the multicenter, observational FINNAKI study, we performed a pilot study among critically ill patients who developed AKI (n = 30) matched to critically ill patients without AKI (n = 30). We explored the urine and plasma levels of cytokeratin-18 neoepitope M30 (CK-18 M30), cell-free DNA, and heat shock protein 70 (HSP70) at intensive care unit (ICU) admission and 24h thereafter, before the clinical diagnosis of AKI defined by the Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes -creatinine and urine output criteria. Furthermore, we performed a validation study in 197 consecutive patients in the FINNAKI cohort and analyzed the urine sample at ICU admission for CK-18 M30 levels.
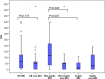
Results: In the pilot study, the urine or plasma levels of measured biomarkers at ICU admission, at 24h, or their maximum value did not differ significantly between AKI and non-AKI patients. Among 20 AKI patients without severe sepsis, the urine CK-18 M30 levels were significantly higher at 24h (median 116.0, IQR [32.3-233.0] U/L) than among those 20 patients who did not develop AKI (46.0 [0.0-54.0] U/L), P = 0.020. Neither urine cell-free DNA nor HSP70 levels significantly differed between AKI and non-AKI patients regardless of the presence of severe sepsis. In the validation study, urine CK-18 M30 level at ICU admission was not significantly higher among patients developing AKI compared to non-AKI patients regardless of the presence of severe sepsis or CKD.
Conclusions: Our findings do not support that apoptosis detected with CK-18 M30 level would be useful in assessing the development of AKI in the critically ill. Urine HSP or cell-free DNA levels did not differ between AKI and non-AKI patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R, Doig GS, Morimatsu H, Morgera S, et al. Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: a multinational, multicenter study. JAMA. 2005;294: 813–8. - PubMed
-
- Chertow GM, Burdick E, Honour M, Bonventre JV, Bates DW. Acute kidney injury, mortality, length of stay, and costs in hospitalized patients. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2005;16: 3365–70. - PubMed
-
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Acute Kidney Injury Work Group. KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury. Kidney inter, Suppl. 2012: 1–138.
-
- Devarajan P. Update on mechanisms of ischemic acute kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17: 1503–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

