microRNAs are differentially regulated between MDM2-positive and negative malignant pleural mesothelioma
- PMID: 26918730
- PMCID: PMC4951323
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.7666
microRNAs are differentially regulated between MDM2-positive and negative malignant pleural mesothelioma
Abstract
Background: Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) is a highly aggressive tumour first-line treated with a combination of cisplatin and pemetrexed. MDM2 and P14/ARF (CDKN2A) are upstream regulators of TP53 and may contribute to its inactivation. In the present study, we now aimed to define the impact of miRNA expression on this mechanism.
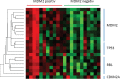
Material and methods: 24 formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tumour specimens were used for miRNA expression analysis of the 800 most important miRNAs using the nCounter technique (NanoString). Significantly deregulated miRNAs were identified before a KEGG-pathway analysis was performed.
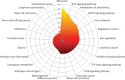
Results: 17 miRNAs regulating TP53, 18 miRNAs regulating MDM2, and 11 miRNAs directly regulating CDKN2A are significantly downregulated in MDM2-expressing mesotheliomas. TP53 is downregulated in MDM2-negative tumours through miRNAs with a miSVR prediction score of 11.67, RB1 with a prediction score of 8.02, MDM2 with a prediction score of 4.50 and CDKN2A with a prediction score of 1.27.
Conclusion: MDM2 expression seems to impact miRNA expression levels in MPM. Especially, miRNAs involved in TP53-signaling are strongly decreased in MDM2-positive mesotheliomas. A better understanding of its tumour biology may open the chance for new therapeutic approaches and thereby augment patients' outcome.
Keywords: MDM2; NanoString nCounter; microRNA; pleural mesothelioma.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors state that they have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Antman KH. Clinical presentation and natural history of benign and malignant mesothelioma. Seminars in oncology. 1981;8:313–320. - PubMed
-
- Hazarika M, White RM, Jr, Booth BP, Wang YC, Ham DY, Liang CY, Rahman A, Gobburu JV, Li N, Sridhara R, Morse DE, Lostritto R, Garvey P, Johnson JR, Pazdur R. Pemetrexed in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Clinical cancer research. 2005;11:982–992. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

