Noncoding RNAs: Regulators of the Mammalian Transcription Machinery
- PMID: 26920110
- PMCID: PMC4894004
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2016.02.019
Noncoding RNAs: Regulators of the Mammalian Transcription Machinery
Abstract
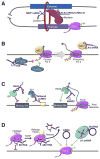
Transcription by RNA polymerase II (Pol II) is required to produce mRNAs and some noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) within mammalian cells. This coordinated process is precisely regulated by multiple factors, including many recently discovered ncRNAs. In this perspective, we will discuss newly identified ncRNAs that facilitate DNA looping, regulate transcription factor binding, mediate promoter-proximal pausing of Pol II, and/or interact with Pol II to modulate transcription. Moreover, we will discuss new roles for ncRNAs, as well as a novel Pol II RNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity that regulates an ncRNA inhibitor of transcription. As the multifaceted nature of ncRNAs continues to be revealed, we believe that many more ncRNA species and functions will be discovered.
Keywords: RNA polymerase II; circular RNAs; divergent RNAs; enhancer RNAs; tethered RNAs.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
TFIIF facilitates dissociation of RNA polymerase II from noncoding RNAs that lack a repression domain.Mol Cell Biol. 2010 Jan;30(1):91-7. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01115-09. Mol Cell Biol. 2010. PMID: 19841064 Free PMC article.
-
RNA polymerase II promoter-proximal pausing in mammalian long non-coding genes.Genomics. 2016 Aug;108(2):64-77. doi: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2016.07.003. Epub 2016 Jul 16. Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27432546 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into transcriptional repression by noncoding RNAs that bind to human Pol II.J Mol Biol. 2013 Oct 9;425(19):3639-48. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2012.08.024. Epub 2012 Sep 4. J Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 22954660 Free PMC article.
-
Role of non-coding RNA transcription around gene regulatory elements in transcription factor recruitment.RNA Biol. 2017 Jan 2;14(1):1-5. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1248020. Epub 2016 Oct 20. RNA Biol. 2017. PMID: 27763805 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-coding-RNA regulators of RNA polymerase II transcription.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Aug;7(8):612-6. doi: 10.1038/nrm1946. Epub 2006 May 24. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16723972 Review.
Cited by
-
Long non-coding RNAs in brain tumours: Focus on recent epigenetic findings in glioma.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Oct;22(10):4597-4610. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13781. Epub 2018 Aug 17. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30117678 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular senescence in cancer: from mechanism paradoxes to precision therapeutics.Mol Cancer. 2025 Aug 8;24(1):213. doi: 10.1186/s12943-025-02419-2. Mol Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40781676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of transcription complexes in the formation of the basal methylation pattern in early development.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Oct 9;115(41):10387-10391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1804755115. Epub 2018 Sep 26. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30257947 Free PMC article.
-
ISR8/IRF1-AS1 Is Relevant for IFNα and NF-κB Responses.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 4;13:829335. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.829335. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35860270 Free PMC article.
-
Nascent RNA signaling to yeast RNA Pol II during transcription elongation.PLoS One. 2018 Mar 23;13(3):e0194438. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194438. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29570714 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

