The MAP kinase pathway coordinates crossover designation with disassembly of synaptonemal complex proteins during meiosis
- PMID: 26920220
- PMCID: PMC4805554
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.12039
The MAP kinase pathway coordinates crossover designation with disassembly of synaptonemal complex proteins during meiosis
Abstract
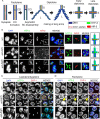
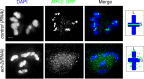
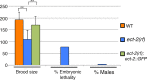
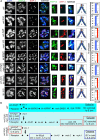
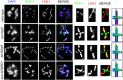
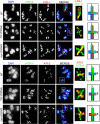
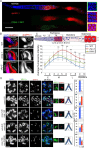
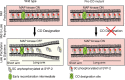
Asymmetric disassembly of the synaptonemal complex (SC) is crucial for proper meiotic chromosome segregation. However, the signaling mechanisms that directly regulate this process are poorly understood. Here we show that the mammalian Rho GEF homolog, ECT-2, functions through the conserved RAS/ERK MAP kinase signaling pathway in the C. elegans germline to regulate the disassembly of SC proteins. We find that SYP-2, a SC central region component, is a potential target for MPK-1-mediated phosphorylation and that constitutively phosphorylated SYP-2 impairs the disassembly of SC proteins from chromosomal domains referred to as the long arms of the bivalents. Inactivation of MAP kinase at late pachytene is critical for timely disassembly of the SC proteins from the long arms, and is dependent on the crossover (CO) promoting factors ZHP-3/RNF212/Zip3 and COSA-1/CNTD1. We propose that the conserved MAP kinase pathway coordinates CO designation with the disassembly of SC proteins to ensure accurate chromosome segregation.
Keywords: c. elegans; MAP kinase; SYP-2; cell biology; chromosomes; crossover recombination; genes; germline; meiosis; synaptonemal complex.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures


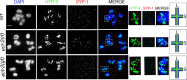
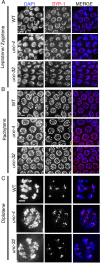

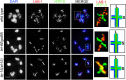
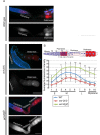



Similar articles
-
ZHP-3 acts at crossovers to couple meiotic recombination with synaptonemal complex disassembly and bivalent formation in C. elegans.PLoS Genet. 2008 Oct;4(10):e1000235. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000235. Epub 2008 Oct 24. PLoS Genet. 2008. PMID: 18949042 Free PMC article.
-
Synaptonemal Complex Central Region Proteins Promote Localization of Pro-crossover Factors to Recombination Events During Caenorhabditis elegans Meiosis.Genetics. 2019 Oct;213(2):395-409. doi: 10.1534/genetics.119.302625. Epub 2019 Aug 20. Genetics. 2019. PMID: 31431470 Free PMC article.
-
C. elegans ZHP-4 is required at multiple distinct steps in the formation of crossovers and their transition to segregation competent chiasmata.PLoS Genet. 2018 Oct 31;14(10):e1007776. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007776. eCollection 2018 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2018. PMID: 30379819 Free PMC article.
-
Zipping and Unzipping: Protein Modifications Regulating Synaptonemal Complex Dynamics.Trends Genet. 2018 Mar;34(3):232-245. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2017.12.001. Epub 2017 Dec 28. Trends Genet. 2018. PMID: 29290403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulating the construction and demolition of the synaptonemal complex.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2016 May 4;23(5):369-77. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.3208. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27142324 Review.
Cited by
-
Actomyosin-mediated apical constriction promotes physiological germ cell death in C. elegans.PLoS Biol. 2024 Aug 23;22(8):e3002775. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002775. eCollection 2024 Aug. PLoS Biol. 2024. PMID: 39178318 Free PMC article.
-
Loss, Gain, and Retention: Mechanisms Driving Late Prophase I Chromosome Remodeling for Accurate Meiotic Chromosome Segregation.Genes (Basel). 2022 Mar 19;13(3):546. doi: 10.3390/genes13030546. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35328099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signaling-Mediated Regulation of Meiotic Prophase I and Transition During Oogenesis.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2017;59:101-123. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-44820-6_4. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2017. PMID: 28247047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ligand-Receptor Interactions Elucidate Sex-Specific Pathways in the Trajectory From Primordial Germ Cells to Gonia During Human Development.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 18;9:661243. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.661243. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34222234 Free PMC article.
-
Oocyte aging is controlled by mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling.Aging Cell. 2021 Jun;20(6):e13386. doi: 10.1111/acel.13386. Epub 2021 Jun 1. Aging Cell. 2021. PMID: 34061407 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arur S, Ohmachi M, Nayak S, Hayes M, Miranda A, Hay A, Golden A, Schedl T. Multiple ERK substrates execute single biological processes in Caenorhabditis elegans germ-line development. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2009;106:4776–4781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0812285106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhalla N, Wynne DJ, Jantsch V, Dernburg AF. Correction: ZHP-3 Acts at Crossovers to Couple Meiotic Recombination with Synaptonemal Complex Disassembly and Bivalent Formation in C. elegans. PLoS Genetics. 2008;4:e12039. doi: 10.1371/annotation/ffbb52bd-7ceb-404c-8c96-93577bf83932. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

