All about that fat: Lipid modification of proteins in Cryptococcus neoformans
- PMID: 26920881
- PMCID: PMC4851765
- DOI: 10.1007/s12275-016-5626-6
All about that fat: Lipid modification of proteins in Cryptococcus neoformans
Abstract
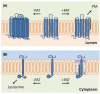
Lipid modification of proteins is a widespread, essential process whereby fatty acids, cholesterol, isoprenoids, phospholipids, or glycosylphospholipids are attached to polypeptides. These hydrophobic groups may affect protein structure, function, localization, and/or stability; as a consequence such modifications play critical regulatory roles in cellular systems. Recent advances in chemical biology and proteomics have allowed the profiling of modified proteins, enabling dissection of the functional consequences of lipid addition. The enzymes that mediate lipid modification are specific for both the lipid and protein substrates, and are conserved from fungi to humans. In this article we review these enzymes, their substrates, and the processes involved in eukaryotic lipid modification of proteins. We further focus on its occurrence in the fungal pathogen Cryptococcus neoformans, highlighting unique features that are both relevant for the biology of the organism and potentially important in the search for new therapies.
Keywords: Cryptococcus; GPI-anchored proteins; isoprenylation; lipid modification; myristoylation; palmitoylation; prenylation; protein lipidation.
Figures



References
-
- Aitken A, Cohen P, Santikarn S, Williams DH, Calder AG, Smith A, Klee CB. Identification of the NH2-terminal blocking group of calcineurin B as myristic acid. FEBS Lett. 1982;150:314–318. - PubMed
-
- Blanc M, Blaskovic S, van der Goot FG. Palmitoylation, pathogens and their host. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2013;41:84–88. - PubMed
-
- Brown GD, Denning DW, Gow NA, Levitz SM, Netea MG, White TC. Hidden killers: human fungal infections. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012;4:165rv113. - PubMed
-
- Caminero A, Calvo E, Valentin E, Ruiz-Herrera J, Lopez JA, Sentandreu R. Identification of Candida albicans wall mannoproteins covalently linked by disulphide and/or alkali-sensitive bridges. Yeast. 2014;31:137–144. - PubMed
-
- Chayakulkeeree M, Sorrell TC, Siafakas AR, Wilson CF, Pantarat N, Gerik KJ, Boadle R, Djordjevic JT. Role and mechanism of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C in survival and virulence of Cryptococcus neoformans. Mol. Microbiol. 2008;69:809–826. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

