A Meta-analysis of Individual Participant Data Reveals an Association between Circulating Levels of IGF-I and Prostate Cancer Risk
- PMID: 26921328
- PMCID: PMC4873385
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-1551
A Meta-analysis of Individual Participant Data Reveals an Association between Circulating Levels of IGF-I and Prostate Cancer Risk
Abstract
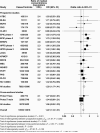
The role of insulin-like growth factors (IGF) in prostate cancer development is not fully understood. To investigate the association between circulating concentrations of IGFs (IGF-I, IGF-II, IGFBP-1, IGFBP-2, and IGFBP-3) and prostate cancer risk, we pooled individual participant data from 17 prospective and two cross-sectional studies, including up to 10,554 prostate cancer cases and 13,618 control participants. Conditional logistic regression was used to estimate the ORs for prostate cancer based on the study-specific fifth of each analyte. Overall, IGF-I, IGF-II, IGFBP-2, and IGFBP-3 concentrations were positively associated with prostate cancer risk (Ptrend all ≤ 0.005), and IGFBP-1 was inversely associated weakly with risk (Ptrend = 0.05). However, heterogeneity between the prospective and cross-sectional studies was evident (Pheterogeneity = 0.03), unless the analyses were restricted to prospective studies (with the exception of IGF-II, Pheterogeneity = 0.02). For prospective studies, the OR for men in the highest versus the lowest fifth of each analyte was 1.29 (95% confidence interval, 1.16-1.43) for IGF-I, 0.81 (0.68-0.96) for IGFBP-1, and 1.25 (1.12-1.40) for IGFBP-3. These associations did not differ significantly by time-to-diagnosis or tumor stage or grade. After mutual adjustment for each of the other analytes, only IGF-I remained associated with risk. Our collaborative study represents the largest pooled analysis of the relationship between prostate cancer risk and circulating concentrations of IGF-I, providing strong evidence that IGF-I is highly likely to be involved in prostate cancer development. Cancer Res; 76(8); 2288-300. ©2016 AACR.
©2016 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures



References
-
- Woodson K, Tangrea JA, Pollak M, Copeland TD, Taylor PR, Virtamo J, et al. Serum insulin-like growth factor I: tumor marker or etiologic factor? A prospective study of prostate cancer among Finnish men. Cancer Research. 2003;63(14):3991–3994. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 16491/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U10 CA037429/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA108964/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA133891/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA033619/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 19170/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- A19169/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- P01 CA055075/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UG1 CA189974/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA182883/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA164973/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA054281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

