MiR-150 Regulates Poststroke Cerebral Angiogenesis via Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Rats
- PMID: 26922365
- PMCID: PMC6492828
- DOI: 10.1111/cns.12525
MiR-150 Regulates Poststroke Cerebral Angiogenesis via Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Rats
Abstract
Aims: Angiogenesis is a harmonized target for poststroke recovery. Therefore, exploring the mechanisms involved in angiogenesis after stroke is vitally significant. In this study, we are reporting a miR-150-based mechanism underlying cerebral poststroke angiogenesis.
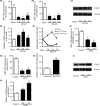
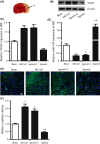
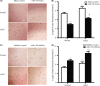
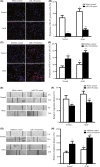
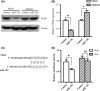
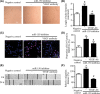
Methods: Rat models of middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) and cell models of oxygen-glucose deprivation were conducted. Capillary density, tube formation, cell proliferation, and cell migration were measured by FITC-dextran assay, matrigel assay, Ki-67 staining, and wound healing assay, respectively. The expression of miR-150 and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) was, respectively, measured by RT-PCR and Western blotting. Dual-luciferase assay was conducted to confirm the binding sites between miR-150 and VEGF.
Results: We found that miR-150 expression in the brain and serum of rats subjected to cerebral ischemia, and in oxygen-glucose-deprived brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMVECs) and astrocytes. Upregulation of miR-150 expression could decrease vascular density of infarct border zone in rat after MCAO and decrease tube formation, proliferation, and migration of BMVECs. We also found that miR-150 could negatively regulate the expression of VEGF, and VEGF was confirmed to be a direct target of miR-150. Moreover, VEGF mediated the function of miR-150 on tube formation, proliferation, and migration of BMVECs.
Conclusions: Our data suggested that miR-150 could regulate cerebral poststroke angiogenesis in rats through VEGF.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Brain microvascular endothelial cells; Stroke; Vascular endothelial growth factor; miR-150.
© 2016 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ferrara N, Kerbel RS. Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target. Nature 2005;438:967–974. - PubMed
-
- Giacca M, Zacchigna S. VEGF gene therapy: therapeutic angiogenesis in the clinic and beyond. Gene Ther 2012;19:622–629. - PubMed
-
- He QW, Xia YP, Chen SC, et al. Astrocyte‐derived sonic hedgehog contributes to angiogenesis in brain microvascular endothelial cells via RhoA/ROCK pathway after oxygen‐glucose deprivation. Mol Neurobiol 2013;47:976–987. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

