Characterization of an Sf-rhabdovirus-negative Spodoptera frugiperda cell line as an alternative host for recombinant protein production in the baculovirus-insect cell system
- PMID: 26923062
- PMCID: PMC4842140
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pep.2016.02.014
Characterization of an Sf-rhabdovirus-negative Spodoptera frugiperda cell line as an alternative host for recombinant protein production in the baculovirus-insect cell system
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Characterization of an Sf-rhabdovirus-negative S. frugiperda cell line as an alternative host for recombinant protein production in the baculovirus-insect cell system" [Protein Expr. Purif. 122 (2016) 45-55].Protein Expr Purif. 2018 Apr;144:39. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2017.12.001. Epub 2017 Dec 8. Protein Expr Purif. 2018. PMID: 29227884 No abstract available.
-
Corrigendum to "Characterization of an Sf-rhabdovirus-negative S. frugiperda cell line as an alternative host for recombinant protein production in the baculovirus-insect cell system" [Protein Expr. Purif. 122 (2016) 45-55].Protein Expr Purif. 2019 Jan;153:44. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2018.08.005. Epub 2018 Aug 21. Protein Expr Purif. 2019. PMID: 30142443 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
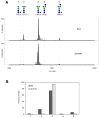
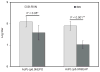
Cell lines derived from the fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda (Sf), are widely used as hosts for recombinant protein production in the baculovirus-insect cell system (BICS). However, it was recently discovered that these cell lines are contaminated with a virus, now known as Sf-rhabdovirus [1]. The detection of this adventitious agent raised a potential safety issue that could adversely impact the BICS as a commercial recombinant protein production platform. Thus, we examined the properties of Sf-RVN, an Sf-rhabdovirus-negative Sf cell line, as a potential alternative host. Nested RT-PCR assays showed Sf-RVN cells had no detectable Sf-rhabdovirus over the course of 60 passages in continuous culture. The general properties of Sf-RVN cells, including their average growth rates, diameters, morphologies, and viabilities after baculovirus infection, were virtually identical to those of Sf9 cells. Baculovirus-infected Sf-RVN and Sf9 cells produced equivalent levels of three recombinant proteins, including an intracellular prokaryotic protein and two secreted eukaryotic glycoproteins, and provided similar N-glycosylation patterns. In fact, except for the absence of Sf-rhabdovirus, the only difference between Sf-RVN and Sf9 cells was SF-RVN produced higher levels of infectious baculovirus progeny. These results show Sf-RVN cells can be used as improved, alternative hosts to circumvent the potential safety hazard associated with the use of Sf-rhabdovirus-contaminated Sf cells for recombinant protein manufacturing with the BICS.
Keywords: Baculovirus; Insect cells; Recombinant protein production; Sf-RVN cells; Sf-rhabdovirus.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
A.B.M. and C.G. are employees and D.L.J. is the President of GlycoBac, LLC. Accordingly, all authors declare potential conflicts of interest as we expect GlycoBac will provide the new cell line reported herein as a commercial product, which will be of financial benefit to the company.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A new insect cell line engineered to produce recombinant glycoproteins with cleavable N-glycans.J Biol Chem. 2022 Jan;298(1):101454. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101454. Epub 2021 Nov 26. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 34838817 Free PMC article.
-
The Spodoptera frugiperda Sf9 cell line is a heterogeneous population of rhabdovirus-infected and virus-negative cells: Isolation and characterization of cell clones containing rhabdovirus X-gene variants and virus-negative cell clones.Virology. 2019 Oct;536:125-133. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2019.08.001. Epub 2019 Aug 2. Virology. 2019. PMID: 31494355
-
A new approach for detecting adventitious viruses shows Sf-rhabdovirus-negative Sf-RVN cells are suitable for safe biologicals production.BMC Biotechnol. 2018 Feb 7;18(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s12896-017-0412-z. BMC Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29415704 Free PMC article.
-
Adventitious viruses in insect cell lines used for recombinant protein expression.Protein Expr Purif. 2018 Apr;144:25-32. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2017.11.002. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Protein Expr Purif. 2018. PMID: 29133148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Baculovirus-insect cell expression systems.Methods Enzymol. 2009;463:191-222. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(09)63014-7. Methods Enzymol. 2009. PMID: 19892174 Review.
Cited by
-
ADDovenom: Thermostable Protein-Based ADDomer Nanoparticles as New Therapeutics for Snakebite Envenoming.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Nov 28;15(12):673. doi: 10.3390/toxins15120673. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38133177 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome analysis of Spodoptera RNA-seq data unveils new viruses within the family Rhabdoviridae.Virus Genes. 2025 Jul 27. doi: 10.1007/s11262-025-02177-9. Online ahead of print. Virus Genes. 2025. PMID: 40715947
-
Complete study demonstrating the absence of rhabdovirus in a distinct Sf9 cell line.PLoS One. 2017 Apr 19;12(4):e0175633. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175633. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28423032 Free PMC article.
-
Rhabdovirus-like endogenous viral elements in the genome of Spodoptera frugiperda insect cells are actively transcribed: Implications for adventitious virus detection.Biologicals. 2016 Jul;44(4):219-225. doi: 10.1016/j.biologicals.2016.04.004. Epub 2016 May 25. Biologicals. 2016. PMID: 27236849 Free PMC article.
-
Host Range and Population Survey of Spodoptera frugiperda Rhabdovirus.J Virol. 2019 Mar 5;93(6):e02028-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02028-18. Print 2019 Mar 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30626676 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van Oers MM, Pijlman GP, Vlak JM. Thirty years of baculovirus-insect cell protein expression: from dark horse to mainstream technology. J Gen Virol. 2015;96:6–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

