The Wild Wild West: A Framework to Integrate mHealth Software Applications and Wearables to Support Physical Activity Assessment, Counseling and Interventions for Cardiovascular Disease Risk Reduction
- PMID: 26923067
- PMCID: PMC5362162
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pcad.2016.02.007
The Wild Wild West: A Framework to Integrate mHealth Software Applications and Wearables to Support Physical Activity Assessment, Counseling and Interventions for Cardiovascular Disease Risk Reduction
Abstract
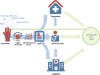
Physical activity (PA) interventions constitute a critical component of cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk reduction programs. Objective mobile health (mHealth) software applications (apps) and wearable activity monitors (WAMs) can advance both assessment and integration of PA counseling in clinical settings and support community-based PA interventions. The use of mHealth technology for CVD risk reduction is promising, but integration into routine clinical care and population health management has proven challenging. The increasing diversity of available technologies and the lack of a comprehensive guiding framework are key barriers for standardizing data collection and integration. This paper reviews the validity, utility and feasibility of implementing mHealth technology in clinical settings and proposes an organizational framework to support PA assessment, counseling and referrals to community resources for CVD risk reduction interventions. This integration framework can be adapted to different clinical population needs. It should also be refined as technologies and regulations advance under an evolving health care system landscape in the United States and globally.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; Clinical counseling; Mobile health; Physical activity; Population health management.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Lobelo is on the advisory board of the American College of Sports Medicine’ Exercise is Medicine initiative; Dr. McConnell is currently on leave from Stanford and employed by Verily Life Sciences.
Figures

References
-
- LeFevre ML, U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Behavioral counseling to promote a healthful diet and physical activity for cardiovascular disease prevention in adults with cardiovascular risk factors: U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement. Ann Intern Med. 2014;161(8):587–593. - PubMed
-
- Sallis R, Franklin B, Joy L, et al. Strategies for promoting physical activity in clinical practice. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2015;57(4):375–386. - PubMed
-
- Arena R, Harrington RA, Després J-P. A message from modern-day healthcare to physical activity and fitness: welcome home! Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2015;57(4):293–295. - PubMed
-
- Coleman KJ, Ngor E, Reynolds K, et al. Initial validation of an exercise “vital sign” in electronic medical records. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2012;44(11):2071–2076. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

