Oxidative mitochondrial DNA damage in peripheral blood mononuclear cells is associated with reduced volumes of hippocampus and subcortical gray matter in chronically HIV-infected patients
- PMID: 26923169
- PMCID: PMC4877028
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mito.2016.02.006
Oxidative mitochondrial DNA damage in peripheral blood mononuclear cells is associated with reduced volumes of hippocampus and subcortical gray matter in chronically HIV-infected patients
Abstract
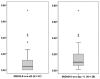
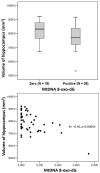
Cross-sectional relationships were examined between regional brain volumes and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) 8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine (8-oxo-dG) in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of 47 HIV patients [mean age 51years; 81% with HIV RNA ≤50copies/mL] on combination antiretroviral therapy. The gene-specific DNA damage and repair assay measured mtDNA 8-oxo-dG break frequency. Magnetic resonance imaging was performed at 3T. Higher mtDNA 8-oxo-dG was associated with lateral ventricular enlargement and with decreased volumes of hippocampus, pallidum, and total subcortical gray matter, suggesting the involvement of systemic mitochondrial-specific oxidative stress in chronic HIV-related structural brain changes and cognitive difficulties. Clarification of the mechanism may provide potential therapeutic targets.
Keywords: Atrophy; Brain; Neuroinflammation; Oxidative stress; Pallidum; ROS.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. and Mitochondria Research Society. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Adle-Biassette H, Chretien F, Wingertsmann L, Hery C, Ereau T, Scaravilli F, Tardieu M, Gray F. Neuronal apoptosis does not correlate with dementia in HIV infection but is related to microglial activation and axonal damage. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 1999;25(2):123–133. - PubMed
-
- Akay C, Cooper M, Odeleye A, Jensen BK, White MG, Vassoler F, Gannon PJ, Mankowski J, Dorsey JL, Buch AM, Cross SA, Cook DR, Pena MM, Andersen ES, Christofidou-Solomidou M, Lindl KA, Zink MC, Clements J, Pierce RC, Kolson DL, Jordan-Sciutto KL. Antiretroviral drugs induce oxidative stress and neuronal damage in the central nervous system. J. Neurovirol. 2014;20(1):39–53. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Almer G, Teismann P, Stevic Z, Halaschek-Wiener J, Deecke L, Kostic V, Przedborski S. Increased levels of the pro-inflammatory prostaglandin PGE2 in CSF from ALS patients. Neurology. 2002;58(8):1277–1279. - PubMed
-
- Andersen JK. Oxidative stress in neurodegeneration: cause or consequence? Nat. Med. 2004;10(Suppl):S18–S25. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

