Partial BACE1 reduction in a Down syndrome mouse model blocks Alzheimer-related endosomal anomalies and cholinergic neurodegeneration: role of APP-CTF
- PMID: 26923405
- PMCID: PMC4773919
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.11.013
Partial BACE1 reduction in a Down syndrome mouse model blocks Alzheimer-related endosomal anomalies and cholinergic neurodegeneration: role of APP-CTF
Abstract
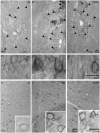
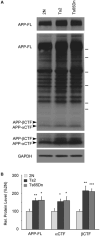
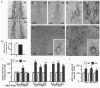
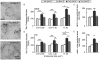
β-amyloid precursor protein (APP) and amyloid beta peptide (Aβ) are strongly implicated in Alzheimer's disease (AD) pathogenesis, although recent evidence has linked APP-βCTF generated by BACE1 (β-APP cleaving enzyme 1) to the development of endocytic abnormalities and cholinergic neurodegeneration in early AD. We show that partial BACE1 genetic reduction prevents these AD-related pathological features in the Ts2 mouse model of Down syndrome. Partially reducing BACE1 by deleting one BACE1 allele blocked development of age-related endosome enlargement in the medial septal nucleus, cerebral cortex, and hippocampus and loss of choline acetyltransferase (ChAT)-positive medial septal nucleus neurons. BACE1 reduction normalized APP-βCTF elevation but did not alter Aβ40 and Aβ42 peptide levels in brain, supporting a critical role in vivo for APP-βCTF in the development of these abnormalities. Although ameliorative effects of BACE1 inhibition on β-amyloidosis and synaptic proteins levels have been previously noted in AD mouse models, our results highlight the additional potential value of BACE1 modulation in therapeutic targeting of endocytic dysfunction and cholinergic neurodegeneration in Down syndrome and AD.
Keywords: APP-βCTF; Alzheimer's disease; BACE1; Basal forebrain cholinergic neurons; Endosomes; Trisomic mice.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Cataldo AM, Mathews PM, Boiteau AB, Hassinger LC, Peterhoff CM, Jiang Y, Mullaney K, Neve RL, Gruenberg J, Nixon RA. Down syndrome fibroblast model of Alzheimer-related endosome pathology. Accelerated endocytosis promotes late endocytic defects. Am J Pathol. 2008;173:370–84. doi:ajpath.2008.071053[pii]10.2353/ajpath.2008.071053. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

