Sulfated Seaweed Polysaccharides as Multifunctional Materials in Drug Delivery Applications
- PMID: 26927134
- PMCID: PMC4820297
- DOI: 10.3390/md14030042
Sulfated Seaweed Polysaccharides as Multifunctional Materials in Drug Delivery Applications
Abstract
In the last decades, the discovery of metabolites from marine resources showing biological activity has increased significantly. Among marine resources, seaweed is a valuable source of structurally diverse bioactive compounds. The cell walls of marine algae are rich in sulfated polysaccharides, including carrageenan in red algae, ulvan in green algae and fucoidan in brown algae. Sulfated polysaccharides have been increasingly studied over the years in the pharmaceutical field, given their potential usefulness in applications such as the design of drug delivery systems. The purpose of this review is to discuss potential applications of these polymers in drug delivery systems, with a focus on carrageenan, ulvan and fucoidan. General information regarding structure, extraction process and physicochemical properties is presented, along with a brief reference to reported biological activities. For each material, specific applications under the scope of drug delivery are described, addressing in privileged manner particulate carriers, as well as hydrogels and beads. A final section approaches the application of sulfated polysaccharides in targeted drug delivery, focusing with particular interest the capacity for macrophage targeting.
Keywords: carrageenan; drug delivery; fucoidan; macrophage targeting; sulfated polysaccharides; ulvan.
Figures

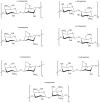




References
-
- Percival E. The polysaccharides of green, red and brown seaweeds: Their basic structure, biosynthesis and function. Br. Phycol. J. 1979;14:103–117. doi: 10.1080/00071617900650121. - DOI
-
- McHugh D.J. A Guide to the Seaweed Industry. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; Rome, Italy: 2003. FAO Fisheries Technical Paper 441.
-
- Mclachlan J. Macroalgae (seaweeds): Industrial resources and their utilization. Plant Soil. 1985;157:137–157. doi: 10.1007/BF02182240. - DOI
-
- Dai-Hung N., Se-Kwon K. Sulfated polysaccharides as bioactive agents from marine algae. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013;62:70–75. - PubMed
-
- Wijesekara I., Pangestuti R., Se-Kwon K. Biological activities and potential health benefits of sulfated polysaccharides derived from marine algae. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011;84:14–21. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.10.062. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

