'Everyone has a secret they keep close to their hearts': challenges faced by adolescents living with HIV infection at the Kenyan coast
- PMID: 26927422
- PMCID: PMC4772469
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-016-2854-y
'Everyone has a secret they keep close to their hearts': challenges faced by adolescents living with HIV infection at the Kenyan coast
Abstract
Background: The upsurge in the uptake of antiretroviral therapy (ART) has led to a significant increase in the survival of vertically acquired HIV infected children, many of whom are currently living into adolescence and early adulthood. However little if anything is known of the lived experiences and the challenges faced by HIV positive adolescents in the African context. We set out to investigate psychosocial challenges faced by HIV infected adolescents on the Kenyan coast.
Methods: A total of 44 participants (12 HIV-infected adolescents, 7 HIV uninfected adolescents, and 25 key informants) took part in this qualitative study, using individually administered in-depth interviews. A framework approach was used to analyze the data using NVIVO software.
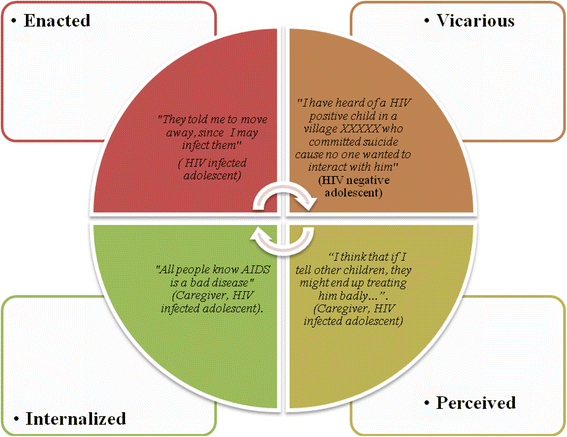
Results: We observed that the challenges faced by adolescents in rural Kenya could be placed into six major themes: poverty, poor mental and physical health, the lack of a school system that is responsive to their needs, challenges in how to disclose to peers and family members, high levels of stigma in its various forms, and challenges of medical adherence leading to the need for close monitoring.
Conclusion: In this African community, vertically acquired HIV-infected adolescents face a complex set of social, economic and medical challenges. Our study points to the urgent need to develop multisectorial intervention support programmes to fully address these challenges.
Figures
References
-
- UNAIDS . Joint United Nations Programme on HIV/AIDS 2012. Geneva: UNAIDS; 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical