Robotic versus laparoscopic low anterior resection for rectal cancer: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 26928124
- PMCID: PMC4772524
- DOI: 10.1186/s12957-016-0816-6
Robotic versus laparoscopic low anterior resection for rectal cancer: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The objective of this meta-analysis was to compare the clinical and oncologic outcomes of robotic low anterior resection (R-LAR) with conventional laparoscopic low anterior resection (L-LAR).
Methods: A search in the MEDLINE, Embase, and Ovid databases was performed for studies published before July 2014 that compared the clinical and oncologic outcomes of R-LAR and L-LAR. The methodological quality of the selected studies was assessed. Depending on statistical heterogeneity, a fixed or random effects model was used for the meta-analysis. The clinical and oncologic outcomes evaluated included operative time, estimated blood loss, length of hospital stay, rate of conversion to open surgery, post-operative complications, circumferential margin status, and number of lymph nodes collected.
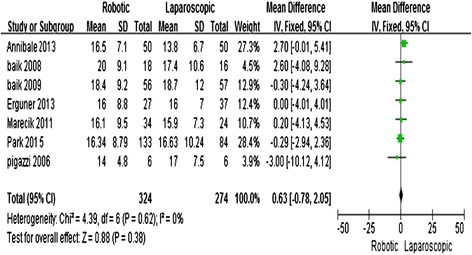
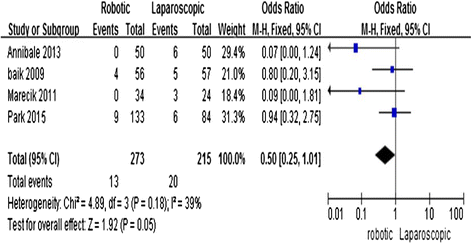
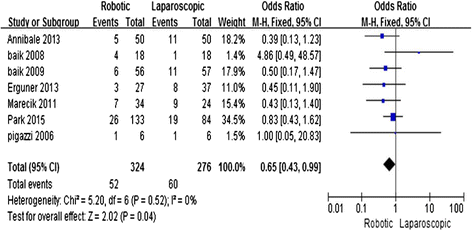
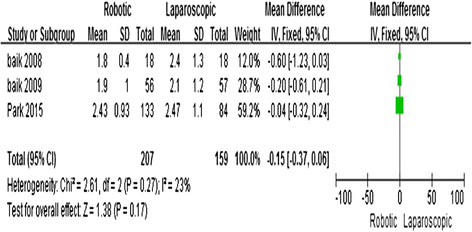
Results: Eight studies, including 324 R-LAR cases and 268 conventional L-LAR cases, were analyzed. The meta-analysis showed that R-LAR was associated with a shorter hospital stay (mean difference (MD) = -1.03; 95% confidence interval (CI) = -1.78, -0.28; P = 0.007), lower conversion rate (odds ratio (OR) = 0.08; 95% CI = 0.02, 0.31; P = 0.0002), lower rate of circumferential margin involvement (OR = 0.5; 95% CI = 0.25, 1.01; P = 0.05), and lower overall complication rate (MD = 0.65; 95% CI = 0.43, 0.99; P = 0.04) compared with L-LAR. There was no difference in operative time (MD = 28.4; 95% CI = -3.48, 60.27; P = 0.08), the number of lymph nodes removed (MD = -0.63; 95% CI = -0.78, 2.05; P = 0.38), and days to return of bowel function (MD = -0.15; 95% CI = -0.37, 0.06; P = 0.17).
Conclusions: R-LAR was shown to be associated with a shorter hospital stay, lower conversion rate, lower rate of circumferential margin involvement, and lower overall complication rate compared with L-LAR. There were no differences in operative time, the number of lymph nodes removed, and days to return of bowel function.
Figures




References
-
- Guillou PJ, Quirke P, Thorpe H, Walker J, Jayne DG, Smith AM, et al. Short-term endpoints of conventional versus laparoscopic-assisted surgery in patients with colorectal cancer (MRC CLASICC trial): multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2005;365:1718–1726. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(05)66545-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cadière GB, Himpens J, Germay O, Izizaw R, Degueldre M, Vandromme J, et al. Feasibility of robotic laparoscopic surgery: 146 cases. World J Surg. 2001;25:1467–1477. - PubMed
-
- Ng KH, Lim YK, Ho KS, Ooi BS, Eu KW. Robotic-assisted surgery for low rectal dissection: from better views to better outcome. Singapore Med J. 2009;50:763–767. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

