Structural and Functional Analysis of a Novel Interaction Motif within UFM1-activating Enzyme 5 (UBA5) Required for Binding to Ubiquitin-like Proteins and Ufmylation
- PMID: 26929408
- PMCID: PMC4861472
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.715474
Structural and Functional Analysis of a Novel Interaction Motif within UFM1-activating Enzyme 5 (UBA5) Required for Binding to Ubiquitin-like Proteins and Ufmylation
Abstract
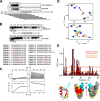
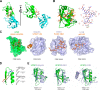
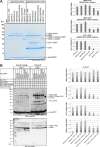
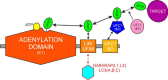
The covalent conjugation of ubiquitin-fold modifier 1 (UFM1) to proteins generates a signal that regulates transcription, response to cell stress, and differentiation. Ufmylation is initiated by ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme 5 (UBA5), which activates and transfers UFM1 to ubiquitin-fold modifier-conjugating enzyme 1 (UFC1). The details of the interaction between UFM1 and UBA5 required for UFM1 activation and its downstream transfer are however unclear. In this study, we described and characterized a combined linear LC3-interacting region/UFM1-interacting motif (LIR/UFIM) within the C terminus of UBA5. This single motif ensures that UBA5 binds both UFM1 and light chain 3/γ-aminobutyric acid receptor-associated proteins (LC3/GABARAP), two ubiquitin (Ub)-like proteins. We demonstrated that LIR/UFIM is required for the full biological activity of UBA5 and for the effective transfer of UFM1 onto UFC1 and a downstream protein substrate both in vitro and in cells. Taken together, our study provides important structural and functional insights into the interaction between UBA5 and Ub-like modifiers, improving the understanding of the biology of the ufmylation pathway.
Keywords: LC3/GABARAP; LIR; UBA5; UFIM; UFM1; isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC); nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR); protein motif; signal transduction; x-ray crystallography.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Kang S. H., Kim G. R., Seong M., Baek S. H., Seol J. H., Bang O. S., Ovaa H., Tatsumi K., Komatsu M., Tanaka K., and Chung C. H. (2007) Two novel ubiquitin-fold modifier 1 (Ufm1)-specific proteases, UfSP1 and UfSP2. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 5256–5262 - PubMed
-
- Yoo H. M., Kang S. H., Kim J. Y., Lee J. E., Seong M. W., Lee S. W., Ka S. H., Sou Y. S., Komatsu M., Tanaka K., Lee S. T., Noh D. Y., Baek S. H., Jeon Y. J., and Chung C. H. (2014) Modification of ASC1 by UFM1 is crucial for ERα transactivation and breast cancer development. Mol. Cell 56, 261–274 - PubMed
-
- Zhang M., Zhu X., Zhang Y., Cai Y., Chen J., Sivaprakasam S., Gurav A., Pi W., Makala L., Wu J., Pace B., Tuan-Lo D., Ganapathy V., Singh N., and Li H. (2015) RCAD/Ufl1, a Ufm1 E3 ligase, is essential for hematopoietic stem cell function and murine hematopoiesis. Cell Death Differ. 22, 1922–1934 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

