A Novel Function of Pet54 in Regulation of Cox1 Synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mitochondria
- PMID: 26929411
- PMCID: PMC4861497
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.721985
A Novel Function of Pet54 in Regulation of Cox1 Synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mitochondria
Abstract
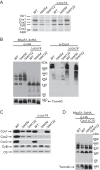
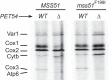
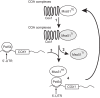
Cytochrome c oxidase assembly requires the synthesis of the mitochondria-encoded core subunits, Cox1, Cox2, and Cox3. In yeast, Pet54 protein is required to activate translation of the COX3 mRNA and to process the aI5β intron on the COX1 transcript. Here we report a third, novel function of Pet54 on Cox1 synthesis. We observed that Pet54 is necessary to achieve an efficient Cox1 synthesis. Translation of the COX1 mRNA is coupled to the assembly of cytochrome c oxidase by a mechanism that involves Mss51. This protein activates translation of the COX1 mRNA by acting on the COX1 5'-UTR, and, in addition, it interacts with the newly synthesized Cox1 protein in high molecular weight complexes that include the factors Coa3 and Cox14. Deletion of Pet54 decreased Cox1 synthesis, and, in contrast to what is commonly observed for other assembly mutants, double deletion of cox14 or coa3 did not recover Cox1 synthesis. Our results show that Pet54 is a positive regulator of Cox1 synthesis that renders Mss51 competent as a translational activator of the COX1 mRNA and that this role is independent of the assembly feedback regulatory loop of Cox1 synthesis. Pet54 may play a role in Mss51 hemylation/conformational change necessary for translational activity. Moreover, Pet54 physically interacts with the COX1 mRNA, and this binding was independent of the presence of Mss51.
Keywords: Cox1; Mss51; cytochrome c oxidase (Complex IV); mitochondria; mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA); translation initiation; translation regulation; yeast.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Dual functions of Mss51 couple synthesis of Cox1 to assembly of cytochrome c oxidase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitochondria.Mol Biol Cell. 2009 Oct;20(20):4371-80. doi: 10.1091/mbc.e09-06-0522. Epub 2009 Aug 26. Mol Biol Cell. 2009. PMID: 19710419 Free PMC article.
-
The carboxyl-terminal end of Cox1 is required for feedback assembly regulation of Cox1 synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitochondria.J Biol Chem. 2010 Nov 5;285(45):34382-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.161976. Epub 2010 Aug 31. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20807763 Free PMC article.
-
Cox25 teams up with Mss51, Ssc1, and Cox14 to regulate mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 expression and assembly in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Biol Chem. 2011 Jan 7;286(1):555-66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.188805. Epub 2010 Nov 10. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21068384 Free PMC article.
-
Biogenesis and assembly of eukaryotic cytochrome c oxidase catalytic core.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jun;1817(6):883-97. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2011.09.005. Epub 2011 Sep 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 21958598 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Control of protein synthesis in yeast mitochondria: the concept of translational activators.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Feb;1833(2):286-94. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2012.03.007. Epub 2012 Mar 16. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 22450032 Review.
Cited by
-
DPC29 promotes post-initiation mitochondrial translation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Feb 22;51(3):1260-1276. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1229. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36620885 Free PMC article.
-
The Cox1 C-terminal domain is a central regulator of cytochrome c oxidase biogenesis in yeast mitochondria.J Biol Chem. 2017 Jun 30;292(26):10912-10925. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.773077. Epub 2017 May 10. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28490636 Free PMC article.
-
The mitospecific domain of Mrp7 (bL27) supports mitochondrial translation during fermentation and is required for effective adaptation to respiration.Mol Biol Cell. 2022 Jan 1;33(1):ar7. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E21-07-0370. Epub 2021 Nov 3. Mol Biol Cell. 2022. PMID: 34731012 Free PMC article.
-
Oms1 associates with cytochrome c oxidase assembly intermediates to stabilize newly synthesized Cox1.Mol Biol Cell. 2016 May 15;27(10):1570-80. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E15-12-0811. Epub 2016 Mar 30. Mol Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27030670 Free PMC article.
-
MrpL35, a mitospecific component of mitoribosomes, plays a key role in cytochrome c oxidase assembly.Mol Biol Cell. 2017 Nov 15;28(24):3489-3499. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E17-04-0239. Epub 2017 Sep 20. Mol Biol Cell. 2017. PMID: 28931599 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siep M., van Oosterum K., Neufeglise H., van der Spek H., and Grivell L. A. (2000) Mss51p, a putative translational activator of cytochrome c oxidase subunit-1 (COX1) mRNA, is required for synthesis of Cox1p in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr. Genet. 37, 213–220 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

