Modulatory Role of Shorea robusta Bark on Glucose-metabolizing Enzymes in Diethylnitrosamine Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Rats
- PMID: 26929587
- PMCID: PMC4745223
- DOI: 10.4103/0973-1296.168981
Modulatory Role of Shorea robusta Bark on Glucose-metabolizing Enzymes in Diethylnitrosamine Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Rats
Abstract
Introduction: The modulations of glucose-metabolizing enzyme activities play a vital rolein the depletion of energy metabolism and leads to inhibition of cancer growth.
Objective: To find the effect of shorearobusta bark extract on glucose-metbolizing enzymes in diethylnitrosamine (DEN) induced hepatocellular carcinoma rats.
Materials and methods: Biochemical evaluation of glucose metabolizing enzyme were done in before and after shorearobusta bark extract (500mg/kg) treatment in DEN induced rats.
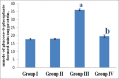
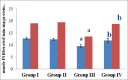
Results: A significant increasein the activities of the key glycolytic enzymes viz., hexokinase and phosphoglucoisomerase, with a significant decrease in the gluconeogenic enzymes glucose-6-phosphatase and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatasewere observed in HCC bearing rats, when compared with the control. Administration of shorearobusta extract caused a significant decrease in theactivities of glycolytic enzymes and an increase in the gluconeogenic enzymes activities to near normal values.
Conclusion: The current findings suggest that the S. robusta extract has a definite modulating role on the key enzymes ofglucose-metabolism in HCC. The modulatory effect may be due to the phytoactive constituents present in the extract of S. robusta.
Summary: Administration of shorea robusta bark extract caused a significant decrease in the activities of glycolytic enzymes and an increase in the gluconeogenic enzymes activities to near normal values. The S. robusta extract has modulatory activity on the carbohydrate metabolism in DEN-induced HCC bearing rats through a mechanism that which does not provoke any acute biochemical disturbances in the metabolic pathways of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. The modulatory effect of S. robusta extract may be attributed to the presence of active compounds such as polyphenols and flavonoids. Abbreviations used: HCC: Hepatocellular Carcinoma, SRBE: Shorearobusta bark extract; HEX: Hexokinase; PGI: Phosphoglucoisomerase; DEN: Diethylnitrosamine.
Keywords: Diethylnitrosamine; Shorea robusta; glucose-metabolizing enzymes; hepatocellular carcinoma.
Figures







References
-
- Cheng YL, Chang WL, Lee SC, Liu YG, Chen CJ, Lin SZ, et al. Acetone extract of Angelica sinensis inhibits proliferation of human cancer cells via inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Life Sci. 2004;75:1579–94. - PubMed
-
- Kirtikar KR, Basu BD, Blatter E, Caius JF, Mahaskar KS. Indian Medicinal Plants. 2nd ed. India: Singh B and Singh MP Publishers; 1980. pp. 288–9.
-
- Prajapati ND, Purohit SS, Sharma AK, Kumar T. A Hand Book of Medicinal Plants. A Complete Source Book. 3rd ed. Jodhpur, India: Agrobios; 2006. p. 474.
-
- Alluri VK, Tayi VN, Sundararaju D, Vanisree M, Hsin-Sheng T, Subbaraju GV. Assessment of bioactivity of Indian medicinal plants using brine shrimp (Artemia saina) lethality assay. Int J Appl Sci Eng. 2005;2:125–34.
-
- Herling A, König M, Bulik S, Holzhütter HG. Enzymatic features of the glucose metabolism in tumor cells. FEBS J. 2011;278:2436–59. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
