Overexpression of eIF4E in colorectal cancer patients is associated with liver metastasis
- PMID: 26929650
- PMCID: PMC4767060
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S98330
Overexpression of eIF4E in colorectal cancer patients is associated with liver metastasis
Abstract
Purpose: Liver metastasis is one of the leading causes of death in colorectal cancer (CRC) patients. The present study aimed to evaluate the value of eIF4E as a prognostic marker of colorectal liver metastasis (CLM) and identify the functional role of eIF4E in CRC metastasis.
Patients and methods: The expression level of eIF4E in CRC tissues was analyzed by immunohistochemical staining and Western blot. Expression of eIF4E in CRC cell lines was evaluated by reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) and Western blot. Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) and Transwell assays were performed to assess the effects of eIF4E on cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Western blot was further used to investigate the mechanism of eIF4E in tumor metastasis.
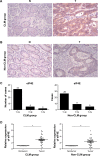
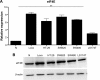
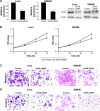
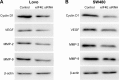
Results: The upregulation frequency of eIF4E in the CLM group (82.5%) was higher than that in the non-CLM group (65.0%). Of the 80 patients recruited for the follow-up study, 23 were in the low eIF4E group (ratio of tumor to nontumor tissue <twofold), and 57 were in the high eIF4E group (ratio of tumor to nontumor tissue ≥twofold). In addition, the group exhibiting high eIF4E expression had a higher rate of liver metastasis (47.4%) than the group exhibiting low eIF4E expression (13.0%). In CRC cell lines, the expression of eIF4E was higher than in the normal cells. In vitro functional studies indicated that eIF4E knockdown inhibited the proliferation, migration, and invasion of Lovo and SW480 cells, and suppressed the expression of cyclin D1, VEGF, MMP-2, and MMP-9.
Conclusion: The results of the present study indicated that high eIF4E levels in CRC patients predicted a high risk of liver metastasis. Knockdown of eIF4E inhibited CRC cell metastasis in part through regulating the expression of cyclin D1, VEGF, MMP-2, and MMP-9.
Keywords: colorectal cancer; eIF4E; functional study; liver metastasis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression analysis and clinical significance of eIF4E, VEGF-C, E-cadherin and MMP-2 in colorectal adenocarcinoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 20;7(51):85502-85514. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13453. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27907907 Free PMC article.
-
Complex Behavior of ALDH1A1 and IGFBP1 in Liver Metastasis from a Colorectal Cancer.PLoS One. 2016 May 6;11(5):e0155160. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0155160. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27152521 Free PMC article.
-
[Abnormal expression of APRIL in colorectal cancer cells promotes tumor growth and metastasis].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2013 Apr;35(4):249-55. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2013.04.003. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 23985251 Chinese.
-
MicroRNA-128 targeting RPN2 inhibits cell proliferation and migration through the Akt-p53-cyclin pathway in colorectal cancer cells.Oncol Lett. 2018 Dec;16(6):6940-6949. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9506. Epub 2018 Sep 26. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30546426 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic and predictive value of long non-coding RNA GAS5 and mircoRNA-221 in colorectal cancer and their effects on colorectal cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion.Cancer Biomark. 2018;22(2):283-299. doi: 10.3233/CBM-171011. Cancer Biomark. 2018. PMID: 29630521
Cited by
-
mTORC1 induces eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E interaction with TOS-S6 kinase 1 and its activation.Cell Cycle. 2021 May;20(9):839-854. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2021.1901038. Epub 2021 May 3. Cell Cycle. 2021. PMID: 33938392 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Protein Synthesis in Colorectal Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2020 May 21;12(5):1298. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051298. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32455578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF4E harnesses hyaluronan production to drive its malignant activity.Elife. 2017 Nov 7;6:e29830. doi: 10.7554/eLife.29830. Elife. 2017. PMID: 29111978 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of the RPSA-Containing and 67EBP Laminin Receptors in Relation to the Debatable Nature of the 67 kDa Laminin Receptor 67LR in Colorectal Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 12;26(6):2564. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062564. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141206 Free PMC article.
-
Surmounting Cancer Drug Resistance: New Perspective on RNA-Binding Proteins.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Aug 7;16(8):1114. doi: 10.3390/ph16081114. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37631029 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel R, Desantis C, Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64(2):104–117. - PubMed
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2015;65(2):87–108. - PubMed
-
- Ueda M, Iguchi T, Nambara S, et al. Overexpression of Transcription Termination Factor 1 is Associated with a Poor Prognosis in Patients with Colorectal Cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2015;22(Suppl 3):1490–1498. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

