Effect of change in patient's bed angles on pain after coronary angiography according to vital signals
- PMID: 26929757
- PMCID: PMC4746866
- DOI: 10.4103/1735-1995.172767
Effect of change in patient's bed angles on pain after coronary angiography according to vital signals
Abstract
Background: One of the most common and important diagnostic methods for the detection of heart diseases is coronary angiography. The aim of this study was to determine the optimum angle of the bed by using vital signals to optimize the patient's position after the angiography.
Materials and methods: This study was a randomized clinical trial (RCT) on participants after angiography who were divided into five groups. The first group was placed routinely in a supine position. In the other groups, all of the patients were placed in bed by angle 15°, 30°, 45°, and 60° upward. In each group, vital signals were measured that included blood pressure, percent of blood oxygen saturation, heart rate, respiratory rate, and temperature. All of measured data compared with the pain score has been achieved from numerical pain scale. The data were analyzed by descriptive statistics method, variance analysis, and post hoc tests in the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) software, version 16. Estimation of the relationship was done by MATLAB version 2011. The level of significance was considered to be 0.05.
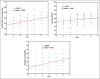
Results: In various groups, there was no significance difference in demographic variables such as gender, age, height, and weight. The mean of pain score, heart rate, systolic blood pressure, and respiratory rate changed significantly (P < 0.05) but the temperature variation, blood oxygen saturation, and diastolic blood pressure in subjects were not significant (P > 0.05). It showed linear changes between pain and systolic blood pressure, respiratory rate, and heart rate changes. A dramatic reduction was also seen in systolic blood pressure, respiratory rate, heart rate, and also pain at an angle of 45(°).
Conclusion: This study showed that, 45(°) was the best angle of the bed to optimize the patient's position after the procedure, based on his/her vital signs and pain score. Thus, in order to relive pain, this change in bed angle is advised to be planned by postangiography nurses in patients after coronary angiography.
Keywords: Coronary angiography; bed position; pain; pain score; vital signals.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of position change on vital signs, back pain and vascular complications following percutaneous coronary intervention.J Clin Nurs. 2019 Apr;28(7-8):1135-1147. doi: 10.1111/jocn.14704. Epub 2018 Nov 22. J Clin Nurs. 2019. PMID: 30367542 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of a multimodal preparation package on vital signs of patients waiting for coronary angiography.Nurs Midwifery Stud. 2014 Apr;3(1):e17518. doi: 10.17795/nmsjournal17518. Epub 2014 Apr 17. Nurs Midwifery Stud. 2014. PMID: 25414893 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of different bed head angles on the hemodynamic parameters of intensive care patients lying in the supine position: A quasi-experimental study.Jpn J Nurs Sci. 2024 Jul;21(3):e12589. doi: 10.1111/jjns.12589. Epub 2024 Feb 13. Jpn J Nurs Sci. 2024. PMID: 38351461
-
Availability and performance of image-based, non-contact methods of monitoring heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and oxygen saturation: a systematic review.Physiol Meas. 2019 Jul 3;40(6):06TR01. doi: 10.1088/1361-6579/ab1f1d. Physiol Meas. 2019. PMID: 31051494
-
[A new approach for studying the retinal and choroidal circulation].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2004 Dec;108(12):836-61; discussion 862. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2004. PMID: 15656089 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
The Effect of Hand Reflexology Massage on Pain and Fatigue in Patients after Coronary Angiography: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial.Nurs Res Pract. 2020 Aug 29;2020:8386167. doi: 10.1155/2020/8386167. eCollection 2020. Nurs Res Pract. 2020. PMID: 32908698 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Patient's Kidney Function Based on Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Criteria and Clinical Parameters in Isolated Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) Surgery in On-Pump and Off-pump Methods in Patients with Low Cardiac Output Syndrome (LCOS) After Surgery.Anesth Pain Med. 2020 Apr 19;10(2):e100517. doi: 10.5812/aapm.100517. eCollection 2020 Apr. Anesth Pain Med. 2020. PMID: 32754433 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of early ambulation on comfort and vascular complications following electrophysiological studies: A randomized controlled trial.J Educ Health Promot. 2024 Aug 29;13:292. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_589_23. eCollection 2024. J Educ Health Promot. 2024. PMID: 39416979 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the effectiveness of position change for patients with pain and vascular complications after transfemoral coronary angiography: a randomized clinical trial.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021 Feb 25;21(1):114. doi: 10.1186/s12872-021-01922-w. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2021. PMID: 33632127 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
An intervention study of a combined intervention of positioning and hand massage in patients undergoing radiofrequency catheter ablation.Nurs Open. 2023 Mar;10(3):1404-1414. doi: 10.1002/nop2.1390. Epub 2022 Sep 25. Nurs Open. 2023. PMID: 36161778 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smeltzer SC, Bare B, Hinkle J L, Cheever KH. Brunner and Suddarth's Text book of Medical- Surgical Nursing. 12th ed. New York: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2010. p. 145.
-
- Farmanbar R, Mohammadiyan MA, Moghaddamniya MT, Kazemnejad E, Salari A. The effect of position change and bed-rest duration after coronary angiography on vascular complications. IJCCN. 2012;4:177–82.
-
- Astin F, Closs SJ, McLenachan J, Hunter S, Priestley C. The information needs of patients treated with primary angioplasty for heart attack: An exploratory study. Patient Educ Couns. 2008;73:325–32. - PubMed
-
- Antman EM, Selwyn AP, Braunwald E, Loscalzo J. Ischemic heart disease. In: Khodaee M, Zinsaz Boroujerdi H, editors. Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine: Disorders of the Cardiovascular System. 17th ed. Tehran: Arjmand Publications; 2008. p. 390.
-
- Kalyani MN, Jamshidi N. Risk factors of Iranian patients with three vessels disease candidate for coronary artery bypass graft surgery (CABG) Pak J Med Sci. 2010;26:837–41.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources