Integrated Analysis of Dysregulated ncRNA and mRNA Expression Profiles in Humans Exposed to Carbon Nanotubes
- PMID: 26930275
- PMCID: PMC4773015
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0150628
Integrated Analysis of Dysregulated ncRNA and mRNA Expression Profiles in Humans Exposed to Carbon Nanotubes
Abstract
Background: As the application of carbon nanotubes (CNT) in consumer products continues to rise, studies have expanded to determine the associated risks of exposure on human and environmental health. In particular, several lines of evidence indicate that exposure to multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) could pose a carcinogenic risk similar to asbestos fibers. However, to date the potential markers of MWCNT exposure are not yet explored in humans.
Methods: In the present study, global mRNA and ncRNA expression profiles in the blood of exposed workers, having direct contact with MWCNT aerosol for at least 6 months (n = 8), were compared with expression profiles of non-exposed (n = 7) workers (e.g., professional and/or technical staff) from the same manufacturing facility.
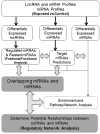
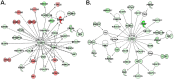
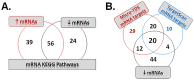
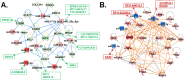
Results: Significant changes in the ncRNA and mRNA expression profiles were observed between exposed and non-exposed worker groups. An integrative analysis of ncRNA-mRNA correlations was performed to identify target genes, functional relationships, and regulatory networks in MWCNT-exposed workers. The coordinated changes in ncRNA and mRNA expression profiles revealed a set of miRNAs and their target genes with roles in cell cycle regulation/progression/control, apoptosis and proliferation. Further, the identified pathways and signaling networks also revealed MWCNT potential to trigger pulmonary and cardiovascular effects as well as carcinogenic outcomes in humans, similar to those previously described in rodents exposed to MWCNTs.
Conclusion: This study is the first to investigate aberrant changes in mRNA and ncRNA expression profiles in the blood of humans exposed to MWCNT. The significant changes in several miRNAs and mRNAs expression as well as their regulatory networks are important for getting molecular insights into the MWCNT-induced toxicity and pathogenesis in humans. Further large-scale prospective studies are necessary to validate the potential applicability of such changes in mRNAs and miRNAs as prognostic markers of MWCNT exposures in humans.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
mRNA and miRNA regulatory networks reflective of multi-walled carbon nanotube-induced lung inflammatory and fibrotic pathologies in mice.Toxicol Sci. 2015 Mar;144(1):51-64. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfu262. Epub 2014 Dec 18. Toxicol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25527334 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory Genes Associated with Pristine Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes-Induced Toxicity in Ocular Cells.Int J Nanomedicine. 2023 May 10;18:2465-2484. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S394694. eCollection 2023. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37192896 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular effects among workers exposed to multiwalled carbon nanotubes.Occup Environ Med. 2018 May;75(5):351-358. doi: 10.1136/oemed-2017-104796. Epub 2018 Feb 10. Occup Environ Med. 2018. PMID: 29440327
-
Genotoxicity and carcinogenicity risk of carbon nanotubes.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013 Dec;65(15):2098-110. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2013.05.011. Epub 2013 Jun 7. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013. PMID: 23751780 Review.
-
Computationally Modeling ncRNA-ncRNA Crosstalk.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1094:77-86. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-0719-5_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 30191489 Review.
Cited by
-
Immunotoxicity of Carbon-Based Nanomaterials, Starring Phagocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 10;23(16):8889. doi: 10.3390/ijms23168889. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012161 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predicting Occupational Exposures to Carbon Nanotubes and Nanofibers Based on Workplace Determinants Modeling.Ann Work Expo Health. 2019 Feb 16;63(2):158-172. doi: 10.1093/annweh/wxy102. Ann Work Expo Health. 2019. PMID: 30715150 Free PMC article.
-
Carbon nanotube and nanofiber exposure and sputum and blood biomarkers of early effect among U.S. workers.Environ Int. 2018 Jul;116:214-228. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2018.04.004. Epub 2018 Apr 23. Environ Int. 2018. PMID: 29698898 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analysis of lung and blood transcriptomes in mice exposed to multi-walled carbon nanotubes.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020 Mar 1;390:114898. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2020.114898. Epub 2020 Jan 22. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31978390 Free PMC article.
-
Do Carbon Nanotubes and Asbestos Fibers Exhibit Common Toxicity Mechanisms?Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 May 17;12(10):1708. doi: 10.3390/nano12101708. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35630938 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mercer RR, Scabilloni J, Wang L, Kisin E, Murray AR, Schwegler-Berry D, et al. Alteration of deposition pattern and pulmonary response as a result of improved dispersion of aspirated single-walled carbon nanotubes in a mouse model. American journal of physiology Lung cellular and molecular physiology. 2008;294(1):L87–97. 10.1152/ajplung.00186.2007 . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

