A Structural Perspective on Readout of Epigenetic Histone and DNA Methylation Marks
- PMID: 26931326
- PMCID: PMC4772102
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a018754
A Structural Perspective on Readout of Epigenetic Histone and DNA Methylation Marks
Abstract
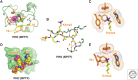
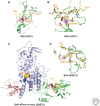
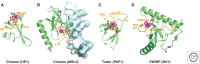
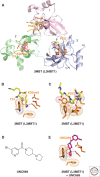
This article outlines the protein modules that target methylated lysine histone marks and 5mC DNA marks, and the molecular principles underlying recognition. The article focuses on the structural basis underlying readout of isolated marks by single reader molecules, as well as multivalent readout of multiple marks by linked reader cassettes at the histone tail and nucleosome level. Additional topics addressed include the role of histone mimics, cross talk between histone marks, technological developments at the genome-wide level, advances using chemical biology approaches, the linkage between histone and DNA methylation, the role for regulatory lncRNAs, and the promise of chromatin-based therapeutic modalities.
Copyright © 2016 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures





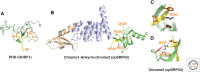
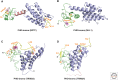



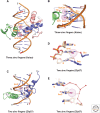
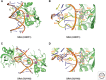
References
-
- Allis CD, Muir TW. 2011. Spreading chromatin into chemical biology. Chembiochem 12: 264–279. - PubMed
-
- Allis CD, Jeuwein T, Reinberg D. 2014. Overview and concepts. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 10.1101/cshperspect.a018739. - DOI
-
- Amir RE, Van den Veyver IB, Wan M, Tran CQ, Francke U, Zoghbi HY. 1999. Rett syndrome is caused by mutations in X-linked MECP2, encoding methyl-CpG-binding protein 2. Nat Genet 23: 185–188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
