ERK Signaling Pathway Is Involved in HPV-16 E6 but not E7 Oncoprotein-Induced HIF-1α Protein Accumulation in NSCLC Cells
- PMID: 26931433
- PMCID: PMC7838632
- DOI: 10.3727/096504015X14496932933610
ERK Signaling Pathway Is Involved in HPV-16 E6 but not E7 Oncoprotein-Induced HIF-1α Protein Accumulation in NSCLC Cells
Abstract
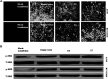
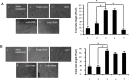
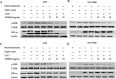
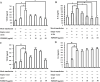
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)1/2 signaling pathway plays a critical role in regulating tumor angiogenesis. Our previous studies have demonstrated that HPV-16 oncoproteins enhanced hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) protein accumulation and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and interleukin-8 (IL-8) expression in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells, thus contributing to angiogenesis. In this study, we further investigated the role of ERK1/2 signaling pathway in HPV-16 oncoprotein-induced HIF-1α, VEGF, and IL-8 expression and in vitro angiogenesis in NSCLC cells. Our results showed that HPV-16 E6 and HPV-16 E7 oncoproteins promoted the activation of ERK1/2 signaling pathway in A549 and NCI-H460 cells. Moreover, PD98059, a specific inhibitor of ERK1/2, blocked in vitro angiogenesis stimulated by HPV-16 E6 but not E7 oncoprotein. Additionally, HIF-1α protein accumulation and VEGF and IL-8 expression in NSCLC cells induced by HPV-16 E6 but not E7 oncoprotein were significantly inhibited by PD98059. Taken together, our results suggest that ERK1/2 signaling pathway is involved in HPV-16 E6 but not E7 oncoprotein-induced HIF-1α, VEGF, and IL-8 expression in NSCLC cells, leading to the enhanced angiogenesis in vitro.
Figures
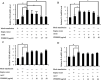
References
-
- Muallaoglu S.; Karadeniz C.; Mertsoylu H.; Ayberk Besen A.; Sezer A.; Murat Sedef A.; Kose F.; Ozyilkan O. The clinicopathological and survival differences between never and ever smokers with non-small cell lung cancer. J. BUON. 19:453–458; 2014. - PubMed
-
- Kawaguchi T.; Takada M.; Kubo A.; Matsumura A.; Fukai S.; Tamura A.; Saito R.; Kawahara M.; Maruyama Y. Gender, histology, and time of diagnosis are important factors for prognosis: Analysis of 1499 never-smokers with advanced non-small cell lung cancer in Japan. J. Thorac. Oncol. 5:1011–1017; 2010. - PubMed
-
- Yano T.; Haro A.; Shikada Y.; Maruyama R.; Maehara Y. Non-small cell lung cancer in never smokers as a representative ‘non-smoking-associated lung cancer’: Epidemiology and clinical features. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 16:287–293; 2011. - PubMed
-
- Wang Y.; Wang A.; Jiang R.; Pan H.; Huang B.; Lu Y.; Wu C. Human papillomavirus type 16 and 18 infection is associated with lung cancer patients from the central part of China. Cancer 121(Suppl. 17):3069–3079; 2015. - PubMed
-
- Fei Y.; Yang J.; Hsieh W. C.; Wu J. Y.; Wu T. C. Different human papillomavirus 16/18 infection in Chinese non-small cell lung cancer patients living in Wuhan, China. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 36:274–279; 2006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
