The HAPPY (Healthy and Active Parenting Programmme for early Years) feasibility randomised control trial: acceptability and feasibility of an intervention to reduce infant obesity
- PMID: 26931491
- PMCID: PMC4774160
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-016-2861-z
The HAPPY (Healthy and Active Parenting Programmme for early Years) feasibility randomised control trial: acceptability and feasibility of an intervention to reduce infant obesity
Abstract
Background: The prevalence of infant obesity is increasing, but there is a lack of evidence-based approaches to prevent obesity at this age. This study tested the acceptability and feasibility of evaluating a theory-based intervention aimed at reducing risk of obesity in infants of overweight/obese women during and after pregnancy: the Healthy and Active Parenting Programme for Early Years (HAPPY).
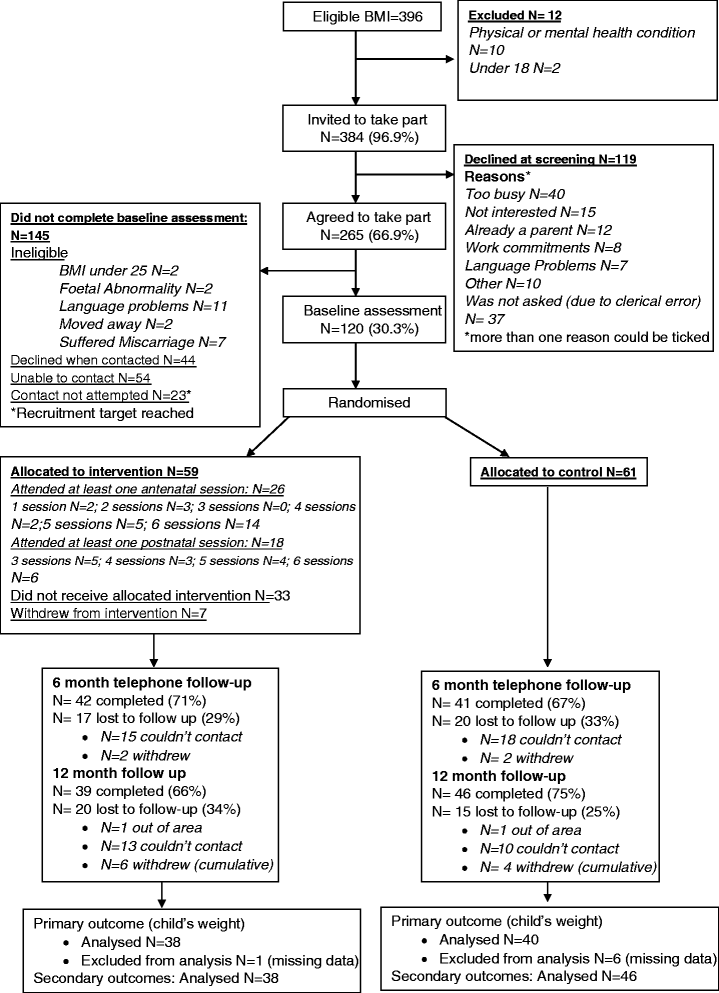
Methods: A feasibility randomised controlled trial was conducted in Bradford, England. One hundred twenty overweight/obese pregnant women (Body Mass Index [BMI] ≥25 kg/m(2)) were recruited between 10-26 weeks gestation. Consenting women were randomly allocated to HAPPY (6 antenatal, 6 postnatal sessions: N = 59) or usual care (N = 61). Appropriate outcome measures for a full trial were explored, including: infant's length and weight, woman's BMI, physical activity and dietary intake of the women and infants. Health economic data were collected. Measurement occurred before randomisation and when the infant was aged 6 months and 12 months. Feasibility outcomes were: recruitment/attrition rates, and acceptability of: randomisation, measurement, and intervention. Intra-class correlations for infant weight were calculated. Fidelity was assessed through observations and facilitator feedback. Focus groups and semi-structured interviews explored acceptability of methods, implementation, and intervention content.
Results: Recruitment targets were met (~20 women/month) with a recruitment rate of 30 % of eligible women (120/396). There was 30 % attrition at 12 months; 66 % of recruited women failed to attend intervention sessions, but those who attended the first session were likely to continue to attend (mean 9.4/12 sessions, range 1-12). Reaction to intervention content was positive, and fidelity was high. Group clustering was minimal; an adjusted effect size of -0.25 standard deviation scores for infant weight at 12 months (95 % CI: -0.16-0.65) favouring the intervention was observed using intention to treat analyses. No adverse events were reported.
Conclusions: The HAPPY intervention appeared feasible and acceptable to participants who attended and those delivering it, however attendance was low; adaptations to increase initial attendance are recommended. Whilst the study was not powered to detect a definitive effect, our results suggest a potential to reduce risk of infant obesity. The evidence reported provides valuable lessons to inform progression to a definitive trial.
Trial registration: Current Controlled Trials ISRCTN56735429.
References
-
- Ng M, Fleming T, Robinson M, et al. Global, regional, and national prevalence of overweight and obesity in children and adults during 1980–2013: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2014 doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(14)60460-8 [published Online First: Epub Date]|. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dietz WH. Childhood weight affects adult morbidity and mortality. J Nutr. 1998;128(2 Suppl):411S–14S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous