FgSsn3 kinase, a component of the mediator complex, is important for sexual reproduction and pathogenesis in Fusarium graminearum
- PMID: 26931632
- PMCID: PMC4773989
- DOI: 10.1038/srep22333
FgSsn3 kinase, a component of the mediator complex, is important for sexual reproduction and pathogenesis in Fusarium graminearum
Abstract
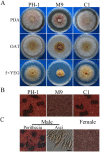
Fusarium graminearum is an important pathogen of wheat and barley. In addition to severe yield losses, infested grains are often contaminated with harmful mycotoxins. In this study, we characterized the functions of FgSSN3 kinase gene in different developmental and infection processes and gene regulation in F. graminearum. The FgSSN3 deletion mutant had a nutrient-dependent growth defects and abnormal conidium morphology. It was significantly reduced in DON production, TRI gene expression, and virulence. Deletion of FgSSN3 also resulted in up-regulation of HTF1 and PCS1 expression in juvenile cultures, and repression of TRI genes in DON-producing cultures. In addition, Fgssn3 was female sterile and defective in hypopodium formation and infectious growth. RNA-seq analysis showed that FgSsn3 is involved in the transcriptional regulation of a wide variety genes acting as either a repressor or activator. FgSsn3 physically interacted with C-type cyclin Cid1 and the cid1 mutant had similar phenotypes with Fgssn3, indicating that FgSsn3 and Cid1 form the CDK-cyclin pair as a component of the mediator complex in F. graminearum. Taken together, our results indicate that FgSSN3 is important for secondary metabolism, sexual reproduction, and plant infection, as a subunit of mediator complex contributing to transcriptional regulation of diverse genes.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The CID1 cyclin C-like gene is important for plant infection in Fusarium graminearum.Fungal Genet Biol. 2010 Feb;47(2):143-51. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2009.11.001. Epub 2009 Nov 10. Fungal Genet Biol. 2010. PMID: 19909822
-
SNARE protein FgVam7 controls growth, asexual and sexual development, and plant infection in Fusarium graminearum.Mol Plant Pathol. 2016 Jan;17(1):108-19. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12267. Epub 2015 May 21. Mol Plant Pathol. 2016. PMID: 25880818 Free PMC article.
-
FgEaf6 regulates virulence, asexual/sexual development and conidial septation in Fusarium graminearum.Curr Genet. 2020 Jun;66(3):517-529. doi: 10.1007/s00294-019-01043-0. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Curr Genet. 2020. PMID: 31728616
-
Advances in Understanding Fusarium graminearum: Genes Involved in the Regulation of Sexual Development, Pathogenesis, and Deoxynivalenol Biosynthesis.Genes (Basel). 2024 Apr 9;15(4):475. doi: 10.3390/genes15040475. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38674409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in genes involved in secondary metabolite synthesis, hyphal development, energy metabolism and pathogenicity in Fusarium graminearum (teleomorph Gibberella zeae).Biotechnol Adv. 2014 Mar-Apr;32(2):390-402. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.12.007. Epub 2014 Jan 2. Biotechnol Adv. 2014. PMID: 24389085 Review.
Cited by
-
The FpPPR1 Gene Encodes a Pentatricopeptide Repeat Protein That Is Essential for Asexual Development, Sporulation, and Pathogenesis in Fusarium pseudograminearum.Front Genet. 2021 Jan 15;11:535622. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.535622. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 33584782 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Transcriptomic Analysis of Race 1 and Race 4 of Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense Induced with Different Carbon Sources.G3 (Bethesda). 2017 Jul 5;7(7):2125-2138. doi: 10.1534/g3.117.042226. G3 (Bethesda). 2017. PMID: 28468818 Free PMC article.
-
Dicer-Like Proteins Regulate Sexual Development via the Biogenesis of Perithecium-Specific MicroRNAs in a Plant Pathogenic Fungus Fusarium graminearum.Front Microbiol. 2018 Apr 26;9:818. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00818. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29755439 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenomic analysis of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (PAL) multigene family and their differential expression analysis in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) suggested their roles during different stress responses.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Sep 30;13:982457. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.982457. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 36247561 Free PMC article.
-
Candida glabrata Med3 Plays a Role in Altering Cell Size and Budding Index To Coordinate Cell Growth.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Jul 17;84(15):e00781-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00781-18. Print 2018 Aug 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29776932 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goswami R. S. & Kistler H. C. Heading for disaster: Fusarium graminearum on cereal crops. Molecular plant pathology 5, 515–525 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Bai G. & Shaner G. Management and resistance in wheat and barley to fusarium head blight. Annual review of phytopathology 42, 135–161 (2004). - PubMed
-
- Proctor R. H., Hohn T. M. & McCormick S. P. Reduced virulence of Gibberella zeae caused by disruption of a trichothecene toxin biosynthetic gene. Molecular plant-microbe interactions : MPMI 8, 593–601 (1995). - PubMed
-
- Desjardins A. E., Bai G., Plattner R. D. & Proctor R. H. Analysis of aberrant virulence of Gibberella zeae following transformation-mediated complementation of a trichothecene-deficient (Tri5) mutant. Microbiology 146 (Pt 8), 2059–2068 (2000). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

