The Cell-Cycle Arrest and Apoptotic Functions of p53 in Tumor Initiation and Progression
- PMID: 26931810
- PMCID: PMC4772082
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a026104
The Cell-Cycle Arrest and Apoptotic Functions of p53 in Tumor Initiation and Progression
Abstract
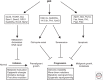
P53 is a transcription factor highly inducible by many stress signals such as DNA damage, oncogene activation, and nutrient deprivation. Cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis are the most prominent outcomes of p53 activation. Many studies showed that p53 cell-cycle and apoptosis functions are important for preventing tumor development. p53 also regulates many cellular processes including metabolism, antioxidant response, and DNA repair. Emerging evidence suggests that these noncanonical p53 activities may also have potent antitumor effects within certain context. This review focuses on the cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis functions of p53, their roles in tumor suppression, and the regulation of cell fate decision after p53 activation.
Copyright © 2016 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bergamaschi D, Samuels Y, O’Neil NJ, Trigiante G, Crook T, Hsieh JK, O’Connor DJ, Zhong S, Campargue I, Tomlinson ML, et al. 2003. iASPP oncoprotein is a key inhibitor of p53 conserved from worm to human. Nat Genet 33: 162–167. - PubMed
-
- Bergamaschi D, Samuels Y, Sullivan A, Zvelebil M, Breyssens H, Bisso A, Del Sal G, Syed N, Smith P, Gasco M, et al. 2006. iASPP preferentially binds p53 proline-rich region and modulates apoptotic function of codon 72-polymorphic p53. Nat Genet 38: 1133–1141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
