Current concepts in the management of rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 26932398
- PMCID: PMC4773729
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2015.137
Current concepts in the management of rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
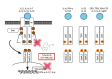
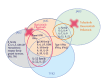
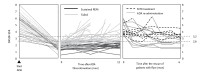
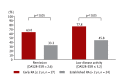
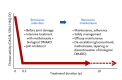
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a systemic autoimmune disease characterized by inflammation and joint destruction that causes significant morbidity and mortality. However, the combined use of methotrexate, a synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD), and biologic DMARD has revolutionized treatment of RA. Clinical remission is now realistic targets, achieved by a large proportion of RA patients, and rapid and appropriate induction of remission by intensive treatment with biological DMARD and methotrexate is prerequisite to halt joint damage and functional disabilities. However, biological DMARD is limited to intravenous or subcutaneous uses and orally available small but strong molecules have been developed. Oral administration of tofacitinib targeting the Janus kinase (JAK) is significantly effective than placebo in active patients with methotrexatenaïve, inadequately responsive to methotrexate or tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-inhibitors. The efficacy was rapid and as strong as adalimumab, a TNF-inhibitor. Meanwhile, association of tofacitinib on carcinogenicity and malignancy is under debate and further investigation on post-marketing survey would be warranted. On the other hand, discontinuation of a biological DMARD without disease flare is our next goal and desirable from the standpoint of risk reduction and cost effectiveness, especially for patients with clinical remission. Recent reports indicate that more than half of early RA patients could discontinue TNF-targeted biological DMARD without clinical flare and functional impairment after obtaining clinical remission. Contrarily, for established RA, fewer patients sustained remission after the discontinuation of biological DMARD and "deep remission" at the discontinuation was a key factor to keep the treatment holiday of biological DMARD.
Keywords: Antirheumatic agents; Arthritis, rheumatoid; Biological antirheumatic agents; Janus kinase inhibitor; Remission.
Conflict of interest statement
Y.T. has received consulting fees, speaking fees, and/or honoraria from Abbvie, Chugai, Astellas, Takeda, Santen, Mitsubishi-Tanabe, Pfizer, Janssen, Eisai, Daiichi-Sankyo, UCB, GlaxoSmithKline, Bristol-Myersand has received research grants from Mitsubishi-Tanabe, Chugai, MSD, Astellas, Novartis. No funding was used to support the writing of the manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- McInnes IB, Schett G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:2205–2219. - PubMed
-
- Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:2569–2581. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
