Nudt3 is an mRNA decapping enzyme that modulates cell migration
- PMID: 26932476
- PMCID: PMC4836651
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.055699.115
Nudt3 is an mRNA decapping enzyme that modulates cell migration
Abstract
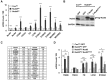
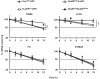
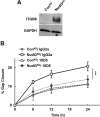
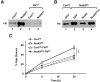
Removal of the 5'-end 7-methylguanosine cap structure is a critical step in the highly regulated process of mRNA decay. The Nudix hydrolase, Dcp2, was identified as a first decapping enzyme and subsequently shown to preferentially modulate stability of only a subset of mRNAs. This observation led to the hypothesis that mammalian cells possess multiple decapping enzymes that may function in distinct pathways. Here we report Nudt3 is a Nudix protein that possesses mRNA decapping activity in cells and is a modulator of MCF-7 breast cancer cell migration. Reduction of Nudt3 protein levels in MCF-7 cells promotes increased cell migration and corresponding enhanced filopodia extensions. Importantly, this phenotype was reversed by complementation with wild type, but not catalytically inactive Nudt3 protein indicating Nudt3 decapping activity normally functions to control cell migration. Genome-wide analysis of Nudt3 compromised cells identified elevated levels of transcripts involved in cell motility including integrin β6, lipocalin-2, and fibronectin. The observed increase in mRNA abundance was dependent on Nudt3 decapping activity where integrin β6 and lipocalin-2 were modulated directly through mRNA stability, while fibronectin was indirectly controlled. Moreover, increased cell migration observed in Nudt3 knockdown cells was mediated through the extracellular integrin β6 and fibronectin protein nexus. We conclude that Nudt3 is an mRNA decapping enzyme that orchestrates expression of a subset of mRNAs to modulate cell migration and further substantiates the existence of multiple decapping enzymes functioning in distinct cellular pathways in mammals.
Keywords: Nudt3; cell motility; fibronectin; integrin β6; mRNA decapping; mRNA stability.
© 2016 Grudzien-Nogalska et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press for the RNA Society.
Figures

Similar articles
-
New insights into decapping enzymes and selective mRNA decay.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2017 Jan;8(1):10.1002/wrna.1379. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1379. Epub 2016 Jul 17. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2017. PMID: 27425147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple Nudix family proteins possess mRNA decapping activity.RNA. 2013 Mar;19(3):390-9. doi: 10.1261/rna.037309.112. Epub 2013 Jan 25. RNA. 2013. PMID: 23353937 Free PMC article.
-
InsP7 is a small-molecule regulator of NUDT3-mediated mRNA decapping and processing-body dynamics.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Aug 11;117(32):19245-19253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1922284117. Epub 2020 Jul 29. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32727897 Free PMC article.
-
The Obesity-Linked Gene Nudt3 Drosophila Homolog Aps Is Associated With Insulin Signaling.Mol Endocrinol. 2015 Sep;29(9):1303-19. doi: 10.1210/ME.2015-1077. Epub 2015 Jul 13. Mol Endocrinol. 2015. PMID: 26168034 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional insights into eukaryotic mRNA decapping.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011 Mar-Apr;2(2):193-208. doi: 10.1002/wrna.44. Epub 2010 Sep 2. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2011. PMID: 21957006 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of Mammalian Nudix Enzymes to Capped RNA Analysis.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Sep 11;17(9):1195. doi: 10.3390/ph17091195. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39338357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Poxvirus Decapping Enzyme Colocalizes with Mitochondria To Regulate RNA Metabolism and Translation and Promote Viral Replication.mBio. 2022 Jun 28;13(3):e0030022. doi: 10.1128/mbio.00300-22. Epub 2022 Apr 18. mBio. 2022. PMID: 35435699 Free PMC article.
-
The inositol pyrophosphate pathway in health and diseases.Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2018 May;93(2):1203-1227. doi: 10.1111/brv.12392. Epub 2017 Dec 27. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2018. PMID: 29282838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predicting the risk of primary Sjögren's syndrome with key N7-methylguanosine-related genes: A novel XGBoost model.Heliyon. 2024 May 16;10(10):e31307. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31307. eCollection 2024 May 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38803884 Free PMC article.
-
CD34-positive pleomorphic uterine sarcoma with NUDT3::RAD51B fusion.Virchows Arch. 2025 Aug;487(2):453-459. doi: 10.1007/s00428-025-04126-1. Epub 2025 May 14. Virchows Arch. 2025. PMID: 40360859
References
-
- Annes JP, Rifkin DB, Munger JS. 2002. The integrin αVβ6 binds and activates latent TGFβ3. FEBS Lett 511: 65–68. - PubMed
-
- Bessman MJ, Frick DN, O'Handley SF. 1996. The MutT proteins or “Nudix” hydrolases, a family of versatile, widely distributed, “housecleaning” enzymes. J Biol Chem 271: 25059–25062. - PubMed
-
- Breuss JM, Gallo J, DeLisser HM, Klimanskaya IV, Folkesson HG, Pittet JF, Nishimura SL, Aldape K, Landers DV, Carpenter W, et al. 1995. Expression of the β6 integrin subunit in development, neoplasia and tissue repair suggests a role in epithelial remodeling. J Cell Sci 108(Pt 6): 2241–2251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
