A comparative view of regenerative neurogenesis in vertebrates
- PMID: 26932669
- PMCID: PMC4813331
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.122796
A comparative view of regenerative neurogenesis in vertebrates
Abstract
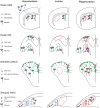
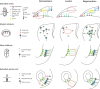
In all vertebrate species studied thus far, the adult central nervous system harbors neural stem cells that sustain constitutive neurogenesis, as well as latent neural progenitors that can be awakened in lesional contexts. In spite of this common theme, many species differ dramatically in their ability to recruit constitutive progenitors, to awaken latent progenitors, or to enhance or bias neural progenitor fate to achieve successful neuronal repair. This Review summarizes the striking similarities in the essential molecular and cellular properties of adult neural stem cells between different vertebrate species, both under physiological and reparative conditions. It also emphasizes the differences in the reparative process across evolution and how the study of non-mammalian models can provide insights into both basic neural stem cell properties and stimulatory cues shared between vertebrates, and subsequent neurogenic events, which are abortive under reparative conditions in mammals.
Keywords: Lesion; Neural stem cells; Neurogenesis; Repair; Zebrafish.
© 2016. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

