KMT2D regulates specific programs in heart development via histone H3 lysine 4 di-methylation
- PMID: 26932671
- PMCID: PMC4813342
- DOI: 10.1242/dev.132688
KMT2D regulates specific programs in heart development via histone H3 lysine 4 di-methylation
Abstract
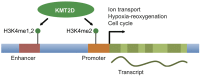
KMT2D, which encodes a histone H3K4 methyltransferase, has been implicated in human congenital heart disease in the context of Kabuki syndrome. However, its role in heart development is not understood. Here, we demonstrate a requirement for KMT2D in cardiac precursors and cardiomyocytes during cardiogenesis in mice. Gene expression analysis revealed downregulation of ion transport and cell cycle genes, leading to altered calcium handling and cell cycle defects. We further determined that myocardial Kmt2d deletion led to decreased H3K4me1 and H3K4me2 at enhancers and promoters. Finally, we identified KMT2D-bound regions in cardiomyocytes, of which a subset was associated with decreased gene expression and decreased H3K4me2 in mutant hearts. This subset included genes related to ion transport, hypoxia-reoxygenation and cell cycle regulation, suggesting that KMT2D is important for these processes. Our findings indicate that KMT2D is essential for regulating cardiac gene expression during heart development primarily via H3K4 di-methylation.
Keywords: ALR; H3K4 methylation; Heart development; KMT2D; Kabuki syndrome; MLL2; MLL4; Mouse.
© 2016. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bernstein B. E., Kamal M., Lindblad-Toh K., Bekiranov S., Bailey D. K., Huebert D. J., McMahon S., Karlsson E. K., Kulbokas E. J., Gingeras T. R. et al. (2005). Genomic maps and comparative analysis of histone modifications in human and mouse. Cell 120, 169-181. 10.1016/j.cell.2005.01.001 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

