SaMpling Antibiotics in Renal Replacement Therapy (SMARRT): an observational pharmacokinetic study in critically ill patients
- PMID: 26932762
- PMCID: PMC4773999
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-016-1421-6
SaMpling Antibiotics in Renal Replacement Therapy (SMARRT): an observational pharmacokinetic study in critically ill patients
Abstract
Background: Optimal antibiotic dosing is key to maximising patient survival, and minimising the emergence of bacterial resistance. Evidence-based antibiotic dosing guidelines for critically ill patients receiving RRT are currently not available, as RRT techniques and settings vary greatly between ICUs and even individual patients. We aim to develop a robust, evidence-based antibiotic dosing guideline for critically ill patients receiving various forms of RRT. We further aim to observe whether therapeutic antibiotic concentrations are associated with reduced 28-day mortality.
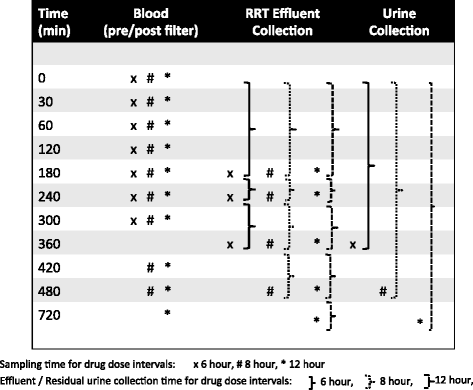
Methods/design: We designed a multi-national, observational pharmacokinetic study in critically ill patients requiring RRT. The study antibiotics will be vancomycin, linezolid, piperacillin/tazobactam and meropenem. Pharmacokinetic sampling of each patient's blood, RRT effluent and urine will take place during two separate dosing intervals. In addition, a comprehensive data set, which includes the patients' demographic and clinical parameters, as well as modality, technique and settings of RRT, will be collected. Pharmacokinetic data will be analysed using a population pharmacokinetic approach to identify covariates associated with changes in pharmacokinetic parameters in critically ill patients with AKI who are undergoing RRT for the five commonly prescribed antibiotics.
Discussion: Using the comprehensive data set collected, the pharmacokinetic profile of the five antibiotics will be constructed, including identification of RRT and other factors indicative of the need for altered antibiotic dosing requirements. This will enable us to develop a dosing guideline for each individual antibiotic that is likely to be relevant to any critically ill patient with acute kidney injury receiving any of the included forms of RRT.
Trial registration: Australian New Zealand Clinical Trial Registry ( ACTRN12613000241730 ) registered 28 February 2013.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Variability of antibiotic concentrations in critically ill patients receiving continuous renal replacement therapy: a multicentre pharmacokinetic study.Crit Care Med. 2012 May;40(5):1523-8. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e318241e553. Crit Care Med. 2012. PMID: 22511133
-
The Effect of Renal Replacement Therapy and Antibiotic Dose on Antibiotic Concentrations in Critically Ill Patients: Data From the Multinational Sampling Antibiotics in Renal Replacement Therapy Study.Clin Infect Dis. 2021 Apr 26;72(8):1369-1378. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa224. Clin Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 32150603
-
The impact of variation in renal replacement therapy settings on piperacillin, meropenem, and vancomycin drug clearance in the critically ill: an analysis of published literature and dosing regimens*.Crit Care Med. 2014 Jul;42(7):1640-50. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000000317. Crit Care Med. 2014. PMID: 24674926
-
Antibiotic dosing in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011 Apr;7(4):226-35. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2011.12. Epub 2011 Feb 22. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 21343897 Review.
-
Antibiotic Dosing in Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy.Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2017 Jul;24(4):219-227. doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2017.05.004. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2017. PMID: 28778361 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Obesity on the Population Pharmacokinetics of Fluconazole in Critically Ill Patients.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016 Oct 21;60(11):6550-6557. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01088-16. Print 2016 Nov. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2016. PMID: 27550344 Free PMC article.
-
A Robust Statistical Approach to Analyse Population Pharmacokinetic Data in Critically Ill Patients Receiving Renal Replacement Therapy.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2019 Feb;58(2):263-270. doi: 10.1007/s40262-018-0690-1. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2019. PMID: 30094712
-
Meropenem and piperacillin/tazobactam optimised dosing regimens for critically ill patients receiving renal replacement therapy.Intensive Care Med. 2025 Aug 13. doi: 10.1007/s00134-025-08067-w. Online ahead of print. Intensive Care Med. 2025. PMID: 40801954
-
Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Considerations of Beta-Lactam Antibiotics in Adult Critically Ill Patients.Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2018 Apr 4;20(5):9. doi: 10.1007/s11908-018-0613-1. Curr Infect Dis Rep. 2018. PMID: 29619607 Review.
-
Therapeutic drug monitoring-guided continuous infusion of piperacillin/tazobactam significantly improves pharmacokinetic target attainment in critically ill patients: a retrospective analysis of four years of clinical experience.Infection. 2019 Dec;47(6):1001-1011. doi: 10.1007/s15010-019-01352-z. Epub 2019 Aug 31. Infection. 2019. PMID: 31473974
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical