Family-wide Characterization of Histone Binding Abilities of Human CW Domain-containing Proteins
- PMID: 26933034
- PMCID: PMC4861470
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M116.718973
Family-wide Characterization of Histone Binding Abilities of Human CW Domain-containing Proteins
Abstract
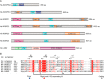
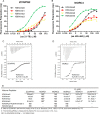
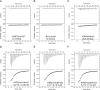
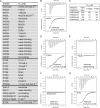
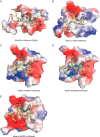
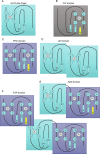
Covalent modifications of histone N-terminal tails play a critical role in regulating chromatin structure and controlling gene expression. These modifications are controlled by histone-modifying enzymes and read out by histone-binding proteins. Numerous proteins have been identified as histone modification readers. Here we report the family-wide characterization of histone binding abilities of human CW domain-containing proteins. We demonstrate that the CW domains in ZCWPW2 and MORC3/4 selectively recognize histone H3 trimethylated at Lys-4, similar to ZCWPW1 reported previously, while the MORC1/2 and LSD2 lack histone H3 Lys-4 binding ability. Our crystal structures of the CW domains of ZCWPW2 and MORC3 in complex with the histone H3 trimethylated at Lys-4 peptide reveal the molecular basis of this interaction. In each complex, two tryptophan residues in the CW domain form the "floor" and "right wall," respectively, of the methyllysine recognition cage. Our mutation results based on ZCWPW2 reveal that the right wall tryptophan residue is essential for binding, and the floor tryptophan residue enhances binding affinity. Our structural and mutational analysis highlights the conserved roles of the cage residues of CW domain across the histone methyllysine binders but also suggests why some CW domains lack histone binding ability.
Keywords: CW domain; H3K4 methylation; MORC3; ZCWPW2; chromatin structure; histone methylation; histone modification; post-translational modification (PTM); protein-protein interaction.
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Vaquero A., Loyola A., and Reinberg D. (2003) The constantly changing face of chromatin. Sci. Aging Knowledge Environ. 2003, RE4. - PubMed
-
- Strahl B. D., and Allis C. D. (2000) The language of covalent histone modifications. Nature 403, 41–45 - PubMed
-
- Adams-Cioaba M. A., and Min J. (2009) Structure and function of histone methylation binding proteins. Biochem. Cell Biol. 87, 93–105 - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y., and Reinberg D. (2001) Transcription regulation by histone methylation: interplay between different covalent modifications of the core histone tails. Genes Dev. 15, 2343–2360 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

