What a Dinner Party! Mechanisms and Functions of Interkingdom Signaling in Host-Pathogen Associations
- PMID: 26933054
- PMCID: PMC4810492
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.01748-15
What a Dinner Party! Mechanisms and Functions of Interkingdom Signaling in Host-Pathogen Associations
Abstract
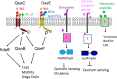
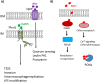
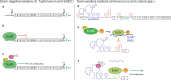
Chemical signaling between cells is an effective way to coordinate behavior within a community. Although cell-to-cell signaling has mostly been studied in single species, it is now appreciated that the sensing of chemical signals across kingdoms can be an important regulator of nutrient acquisition, virulence, and host defense. In this review, we focus on the role of interkingdom signaling in the interactions that occur between bacterial pathogens and their mammalian hosts. We discuss the quorum-sensing (QS) systems and other mechanisms used by these bacteria to sense, respond to, and modulate host signals that include hormones, immune factors, and nutrients. We also describe cross talk between these signaling pathways and strategies used by the host to interfere with bacterial signaling, highlighting the complex bidirectional signaling networks that are established across kingdoms.
Copyright © 2016 Kendall and Sperandio.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Convergence of hormones and autoinducers at the host/pathogen interface.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2007 Jan;387(2):425-35. doi: 10.1007/s00216-006-0694-9. Epub 2006 Aug 16. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2007. PMID: 16912860 Review.
-
Exploitation of host signaling pathways by microbial quorum sensing signals.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2012 Apr;15(2):162-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2011.12.003. Epub 2011 Dec 26. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22204809 Review.
-
Interkingdom signaling between pathogenic bacteria and Caenorhabditis elegans.Trends Microbiol. 2010 Oct;18(10):448-54. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2010.07.002. Epub 2010 Jul 29. Trends Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20667738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interkingdom signaling in plant-microbe interactions.Sci China Life Sci. 2017 Aug;60(8):785-796. doi: 10.1007/s11427-017-9092-3. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Sci China Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28755299 Review.
-
Bacterial manipulation of innate immunity to promote infection.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010 Feb;8(2):117-28. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2295. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20075926 Review.
Cited by
-
Julian Davies and the discovery of kanamycin resistance transposon Tn5.J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2017 Apr;70(4):339-346. doi: 10.1038/ja.2016.120. Epub 2016 Oct 12. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2017. PMID: 27731334 Review.
-
The Norepinephrine Metabolite 3,4-Dihydroxymandelic Acid Is Produced by the Commensal Microbiota and Promotes Chemotaxis and Virulence Gene Expression in Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli.Infect Immun. 2017 Sep 20;85(10):e00431-17. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00431-17. Print 2017 Oct. Infect Immun. 2017. PMID: 28717028 Free PMC article.
-
Quorum Sensing Autoinducer-3 Finally Yields to Structural Elucidation.ACS Cent Sci. 2020 Feb 26;6(2):93-96. doi: 10.1021/acscentsci.0c00033. Epub 2020 Feb 12. ACS Cent Sci. 2020. PMID: 32123727 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Molecules-mediated bidirectional interactions between microbes and human cells.NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2025 Mar 4;11(1):38. doi: 10.1038/s41522-025-00657-2. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes. 2025. PMID: 40038292 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial Microcompartments Coupled with Extracellular Electron Transfer Drive the Anaerobic Utilization of Ethanolamine in Listeria monocytogenes.mSystems. 2021 Apr 13;6(2):e01349-20. doi: 10.1128/mSystems.01349-20. mSystems. 2021. PMID: 33850044 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

