Shaping the Growth Behaviour of Biofilms Initiated from Bacterial Aggregates
- PMID: 26934187
- PMCID: PMC4774936
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149683
Shaping the Growth Behaviour of Biofilms Initiated from Bacterial Aggregates
Erratum in
-
Correction: Shaping the Growth Behaviour of Biofilms Initiated from Bacterial Aggregates.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 27;11(4):e0154637. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154637. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27119152 Free PMC article.
Abstract
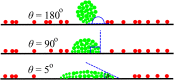
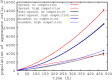
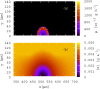
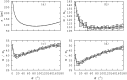
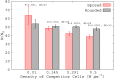
Bacterial biofilms are usually assumed to originate from individual cells deposited on a surface. However, many biofilm-forming bacteria tend to aggregate in the planktonic phase so that it is possible that many natural and infectious biofilms originate wholly or partially from pre-formed cell aggregates. Here, we use agent-based computer simulations to investigate the role of pre-formed aggregates in biofilm development. Focusing on the initial shape the aggregate forms on the surface, we find that the degree of spreading of an aggregate on a surface can play an important role in determining its eventual fate during biofilm development. Specifically, initially spread aggregates perform better when competition with surrounding unaggregated bacterial cells is low, while initially rounded aggregates perform better when competition with surrounding unaggregated cells is high. These contrasting outcomes are governed by a trade-off between aggregate surface area and height. Our results provide new insight into biofilm formation and development, and reveal new factors that may be at play in the social evolution of biofilm communities.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Costerton JW, Montanaro L, Arciola CR. Biofilm in implant infections: Its production and regulation. Int J Artif Organs. 2005;28:1062–1068. - PubMed
-
- Burmølle M, Thomsen TR, Fazli M, Dige I, Christensen L, Homøe P, et al. Biofilms in chronic infections—a matter of opportunity—monospecies biofilms in multispecies infections. FEMS Immunol Med Mic. 2010;59:324–36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

