The influence of (central) auditory processing disorder on the severity of speech-sound disorders in children
- PMID: 26934233
- PMCID: PMC4760364
- DOI: 10.6061/clinics/2016(02)02
The influence of (central) auditory processing disorder on the severity of speech-sound disorders in children
Abstract
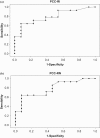
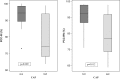
Objective: To identify a cutoff value based on the Percentage of Consonants Correct-Revised index that could indicate the likelihood of a child with a speech-sound disorder also having a (central) auditory processing disorder .
Methods: Language, audiological and (central) auditory processing evaluations were administered. The participants were 27 subjects with speech-sound disorders aged 7 to 10 years and 11 months who were divided into two different groups according to their (central) auditory processing evaluation results.
Results: When a (central) auditory processing disorder was present in association with a speech disorder, the children tended to have lower scores on phonological assessments. A greater severity of speech disorder was related to a greater probability of the child having a (central) auditory processing disorder. The use of a cutoff value for the Percentage of Consonants Correct-Revised index successfully distinguished between children with and without a (central) auditory processing disorder.
Conclusions: The severity of speech-sound disorder in children was influenced by the presence of (central) auditory processing disorder. The attempt to identify a cutoff value based on a severity index was successful.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported.
Figures

References
-
- Wertzner HF, Santos PI, Pagan-Neves LO. Speech errors in children with speech sound disorders according to otitis media history. Rev Soc Bras Fonoaudiol. 2012;17((4)):422–9. - DOI
-
- Wertzner HF, Pagan-Neves LO. Effectiveness of complementary tests in monitoring therapeutic intervention in speech sound disorders. Rev Soc Bras Fonoaudiol. 2012;17((4)):469–75. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

