Ultrasonography for diagnosis of alcoholic cirrhosis in people with alcoholic liver disease
- PMID: 26934429
- PMCID: PMC6464787
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD011602.pub2
Ultrasonography for diagnosis of alcoholic cirrhosis in people with alcoholic liver disease
Abstract
Background: Heavy alcohol consumption causes alcoholic liver disease and is a causal factor of many types of liver injuries and concomitant diseases. It is a true systemic disease that may damage the digestive tract, the nervous system, the heart and vascular system, the bone and skeletal muscle system, and the endocrine and immune system, and can lead to cancer. Liver damage in turn, can present as multiple alcoholic liver diseases, including fatty liver, steatohepatitis, fibrosis, alcoholic cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma, with presence or absence of hepatitis B or C virus infection. There are three scarring types (fibrosis) that are most commonly found in alcoholic liver disease: centrilobular scarring, pericellular fibrosis, and periportal fibrosis. When liver fibrosis progresses, alcoholic cirrhosis occurs. Hepatocellular carcinoma occurs in 5% to 15% of people with alcoholic cirrhosis, but people in whom hepatocellular carcinoma has developed are often co-infected with hepatitis B or C virus.Abstinence from alcohol may help people with alcoholic disease in improving their prognosis of survival at any stage of their disease; however, the more advanced the stage, the higher the risk of complications, co-morbidities, and mortality, and lesser the effect of abstinence. Being abstinent one month after diagnosis of early cirrhosis will improve the chance of a seven-year life expectancy by 1.6 times. Liver transplantation is the only radical method that may change the prognosis of a person with alcoholic liver disease; however, besides the difficulties of finding a suitable liver transplant organ, there are many other factors that may influence a person's survival.Ultrasound is an inexpensive method that has been used for years in clinical practice to diagnose alcoholic cirrhosis. Ultrasound parameters for assessing cirrhosis in people with alcoholic liver disease encompass among others liver size, bluntness of the liver edge, coarseness of the liver parenchyma, nodularity of the liver surface, size of the lymph nodes around the hepatic artery, irregularity and narrowness of the inferior vena cava, portal vein velocity, and spleen size.Diagnosis of cirrhosis by ultrasound, especially in people who are asymptomatic, may have its advantages for the prognosis, motivation, and treatment of these people to decrease their alcohol consumption or become abstinent.Timely diagnosis of alcoholic cirrhosis in people with alcoholic liver disease is the cornerstone for evaluation of prognosis or choosing treatment strategies.
Objectives: To determine the diagnostic accuracy of ultrasonography for detecting the presence or absence of cirrhosis in people with alcoholic liver disease compared with liver biopsy as reference standard.To determine the diagnostic accuracy of any of the ultrasonography tests, B-mode or echo-colour Doppler ultrasonography, used singly or combined, or plus ultrasonography signs, or a combination of these, for detecting hepatic cirrhosis in people with alcoholic liver disease compared with liver biopsy as a reference standard, irrespective of sequence.
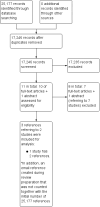
Search methods: We performed searches in The Cochrane Hepato-Biliary Group Controlled Trials Register, The Cochrane Hepato-Biliary Group Diagnostic Test Accuracy Studies Register, The Cochrane Library (Wiley), MEDLINE (OvidSP), EMBASE (OvidSP), and the Science Citation Index Expanded to 8 January 2015. We applied no language limitations.We screened study references of the retrieved studies to identify other potentially relevant studies for inclusion in the review and read abstract and poster publications.
Selection criteria: Three review authors independently identified studies for possible inclusion in the review. We excluded references not fulfilling the inclusion criteria of the review protocol. We sent e-mails to study authors.The included studies had to evaluate ultrasound in the diagnosis of hepatic cirrhosis using only liver biopsy as the reference standard.The maximum time interval of investigation with liver biopsy and ultrasonography should not have exceeded six months. In addition, ultrasonography could have been performed before or after liver biopsy.
Data collection and analysis: We followed the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Diagnostic Test Accuracy.
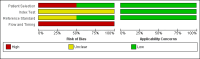
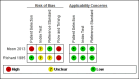
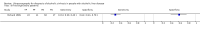
Main results: The review included two studies that provided numerical data regarding alcoholic cirrhosis in 205 men and women with alcoholic liver disease. Although there were no applicability concerns in terms of participant selection, index text, and reference standard, we judged the two studies at high risk of bias. Participants in both studies had undergone both liver biopsy and ultrasonography investigations. The studies shared only a few comparable clinical signs and symptoms (index tests).We decided to not perform a meta-analysis due to the high risk of bias and the high degree of heterogeneity of the included studies.
Authors' conclusions: As the accuracy of ultrasonography in the two included studies was not informative enough, we could not recommend the use of ultrasonography as a diagnostic tool for liver cirrhosis in people with alcoholic liver disease. In order to be able to answer the review questions, we need diagnostic ultrasonography prospective studies of adequate sample size, enrolling only participants with alcoholic liver disease.The design and report of the studies should follow the Standards for Reporting of Diagnostic Accuracy. The sonographic features, with validated cut-offs, which may help identify clinical signs used for diagnosis of fibrosis in alcoholic liver disease, should be carefully selected to achieve maximum diagnostic accuracy on ultrasonography.
Conflict of interest statement
Chavdar Pavlov: none known. Giovanni Casazza: none known. Marianna Semenistaya (earlier Pavlova): none known. Dimitrinka Nikolova: none known. Emmanuel Tsochatzis: none known. Ekaterina Lusina: none known. Vladimir T Ivashkin: none known. Christian Gluud: none known.
Figures












Update of
- doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011602
Similar articles
-
Transient elastography for diagnosis of stages of hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis in people with alcoholic liver disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Jan 22;1(1):CD010542. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010542.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 25612182 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet count, spleen length, and platelet count-to-spleen length ratio for the diagnosis of oesophageal varices in people with chronic liver disease or portal vein thrombosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Apr 26;4(4):CD008759. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008759.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28444987 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in adults with chronic liver disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 6;5(5):CD014798. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014798.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35521901 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Computed tomography for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in adults with chronic liver disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Oct 6;10(10):CD013362. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013362.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34611889 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Prognostic value of the controlling nutritional status (CONUT) score in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma patients especially who had long-time alcohol consumption.J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2020 Nov;67(3):323-331. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.20-27. Epub 2020 May 15. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2020. PMID: 33293775 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms behind the inhibitory effects of ginsenoside Rg3 on hepatic fibrosis: a review.Arch Toxicol. 2025 Feb;99(2):541-561. doi: 10.1007/s00204-024-03941-w. Epub 2024 Dec 27. Arch Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 39729114 Review.
-
Assessment of liver disease in patients with chronic hepatitis C and unhealthy alcohol use.World J Gastroenterol. 2021 Jun 21;27(23):3223-3237. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i23.3223. World J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 34163107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Clinical Algorithm for Screening Compensated Advanced Chronic Liver Disease Utilizing Ultrasonography, Platelet Count, and Albumin Levels, With Transient Elastography as Reference.Cureus. 2024 Nov 17;16(11):e73879. doi: 10.7759/cureus.73879. eCollection 2024 Nov. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39559436 Free PMC article.
-
Association of IL-8 and CXCR2 with AST/ALT Ratio in Liver Abnormalities Screening during Oxidative Stress Injury Caused by VCM.J Toxicol. 2024 Jul 30;2024:1951046. doi: 10.1155/2024/1951046. eCollection 2024. J Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39108287 Free PMC article.
References
References to studies included in this review
Moon 2013 {published data only}
-
- Jo KW, Baik SK, Kim MY, Park SY, Kim BR, Hong JH, et al. The comparison of the usefulness in prediction of advanced fibrosis between the Ultrasonographic Scoring System (USS) and Liver Stiffness Measurement (LSM) in alcohol related liver disease. Hepatology International 2012:250.
Richard 1985 {published data only}
-
- Richard PH, Bonniaud P, Barthelemy C. The accuracy of ultrasound in the diagnosis of cirrhosis. A prospective study of 128 patients [French]. Journal of Radiology 1985;66(8‐9):503‐6. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Aubè 1999 {published data only}
-
- Aubé C, Oberti F, Nouri Korali N, Namour MA, Loisel D, Tanguy JY, et al. Ultrasonographic diagnosis of hepatic fibrosis or cirrhosis. Journal of Hepatology 1999;30:472M‐8M. - PubMed
Colli 2003 {published data only}
-
- Colli A, Fraquelli M, Andreoletti M, Marino B, Zuccoli E, Conte D. Severe liver fibrosis or cirrhosis: accuracy of US for detection ‐‐ analysis of 300 cases. Radiology 2003;227(1):89‐94. - PubMed
Ferral 1992 {published data only}
-
- Ferral H, Male R, Cardiel M, Munoz L, Quiroz y Ferrari F. Cirrhosis: diagnosis by liver surface analysis with high‐frequency ultrasound. Gastrointestinal Radiology 1992;17(1):74‐8. - PubMed
Gaiani 1997 {published data only}
-
- Gaiani S, Gramantieri L, Venturoli N, Piscaglia F, Siringo S, D'Errico A, et al. What is the criterion for differentiating chronic hepatitis from compensated cirrhosis? A prospective study comparing ultrasonography and percutaneous liver biopsy. Journal of Hepatology 1997;27:979‐85. - PubMed
Joseph 1991 {published data only}
-
- Joseph AE, Saverymuttu SH, al‐Sam S, Cook MG, Maxwell JD. Comparison of liver histology with ultrasonography in assessing diffuse parenchymal liver disease. Journal of the Faculty of Radiologists 1991;43(1):26‐31. - PubMed
Kim 2013 {published data only}
-
- Kim MY, Baik SK, Kim HA, Kang HW, Hwang HK, Jo JM, et al. Hepatic vein arrival times using a microbubble contrast ultrasonography can predict disease severity non‐invasively in patients with alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology International 2013:S493‐4.
-
- Kim MY, Suk SK, Baik SK, Kim HA, Kim YJ, Cha SH, et al. Hepatic vein arrival time as assessed by contrast‐enhanced ultrasonography is useful for the assessment of portal hypertension incompensated cirrhosis. Hepatology 2012;56(3):1053‐62. - PubMed
Additional references
Amato 2010
Angulo 2009
-
- Angulo P. Noninvasive assessment of fibrosis and steatosis in NASH and ASH. Gastroenterologie Clinique et Biologique 2009;33(10‐11):940‐8. - PubMed
Bamber 1979
-
- Bamber JC, Hill CR, King JA, Dunn F. Ultrasonic propagation through fixed and unfixed tissues. Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology 1979;5:159‐65. - PubMed
Becker 1996
-
- Becker U, Deis A, Sorensen TI, Gronbaek M, Borch‐Johnsen K, Muller CF, et al. Prediction of risk of liver disease by alcohol intake, sex, and age: a prospective population study. Hepatology 1996;23(5):1025‐9. - PubMed
Bedossa 2003
-
- Bedossa P, Dargère D, Paradis V. Sampling variability of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2003;38(6):1449‐57. - PubMed
Bercoff 2004
-
- Bercoff J, Tanter M, Fink M. Supersonic shear imaging: a new technique for soft tissue elasticity imaging. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics and Frequency Control 2004;51(4):396‐409. - PubMed
Borowsky 1981
-
- Borowsky SA, Strome S, Lott E. Continued heavy drinking and survival in alcoholic cirrhotics. Gastroenterology 1981;80(6):1405‐9. - PubMed
Bouchier 1992
-
- Bouchier IA, Hislop WS, Prescott RJ. A prospective study of alcoholic liver disease and mortality. Journal of Hepatology 1992;16:290‐7. - PubMed
Bruha 2012
Brunt 1974
Brunt 1999
-
- Brunt EM, Janney CG, Bisceglie AM, Neuschwander‐Tetri BA, Bacon BR. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: a proposal for grading and staging the histological lesions. American Journal of Gastroenterology 1999;94(9):2467‐74. - PubMed
Colloredo 2003
-
- Colloredo G, Guido M, Sonzogni A, Leandro G. Impact of liver biopsy size on histological evaluation of chronic viral hepatitis: the smaller the sample, the milder the disease. Journal of Hepatology 2003;39(2):239‐44. - PubMed
Crespo 2012
-
- Crespo G, Fernandez‐Varo G, Marino Z, Casals G, Miquel R, Martinez SM, et al. ARFI, FibroScan, ELF, and their combinations in the assessment of liver fibrosis: a prospective study. Journal of Hepatology 2012;57(2):281‐7. - PubMed
de Vet 2010
-
- Vet HCW, Eisinga A, Riphagen II, Aertgeerts B, Pewsner D. Chapter 7: Searching for studies. In: Deeks JJ, Bossuyt PM, Gatsonis C (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Version 1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2010. Available from srdta.cochrane.org/.
Deeks 2005
-
- Deeks JJ, Macaskill P, Irwig L. The performance of tests of publication bias and other sample size effects in systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy was assessed. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2005;58(9):882‐93. [PUBMED: 16085191] - PubMed
Desmet 1994
-
- Desmet VJ, Gerber M, Hoofnagle JH, Manns M, Scheuer PJ. Classification of chronic hepatitis: diagnosis, grading and staging. Hepatology 1994;19:1513‐20. - PubMed
Ersoz 1999
-
- Ersoz G, Demir A, Akarca OS, Yilmaz F, Ozutemiz O, Karasu Z, et al. The value of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of early cirrhosis. Turkish Journal of Gastroenterology 1999;10(1):7‐10.
Franciscus 2007
-
- Franciscus A. HCV diagnostic tools: grading and staging a liver biopsy version 2.2, 2007. www.hcvadvocate.org (accessed 11 November 2015).
Goodman 2007
-
- Goodman ZD. Grading and staging systems for inflammation and fibrosis in chronic liver diseases. Journal of Hepatology 2007;47(4):598‐607. - PubMed
Grant 1999
Gómez‐Domínguez 2006
-
- Gómez‐Domínguez E, Mendoza J, Rubio S, Moreno‐Monteagudo JA, García‐Buey L, Moreno‐Otero R. Transient elastography: a valid alternative to biopsy in patients with chronic liver disease. Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2006;24(3):513‐8. - PubMed
Haque 2010
-
- Haque M, Robinson C, Owen D, Yoshida EM, Harris A. Comparison of acoustic radiation force impulse imaging (ARFI) to liver biopsy histologic scores in the evaluation of chronic liver disease: a pilot study. Annals of Hepatology 2010;9(3):289‐93. - PubMed
Hizli 2010
-
- Hizli S, Kocyigit A, Arslan N, Tuncel S, Demircioglu F, Cakmakci H, et al. The role of ultrasonographic hepatic artery resistive index in the diagnosis of insulin resistance in obese children with non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease. Turkish Journal of Medical Sciences 2010;40(3):335‐42.
Iruzubieta 2013
Ishak 1995
-
- Ishak K, Baptista A, Bianchi L, Callea F, Groote J, Gudat F, et al. Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis. Journal of Hepatology 1995;22:696‐9. - PubMed
Ismail 2011
Ivashkin 2011a
-
- Ivashkin VT, Pavlov CS. Non‐invasive diagnostic of liver fibrosis. In: Ivashkin VT, Pavlov CS editor(s). Liver Fibrosis. Moscow: Geotar‐Media, 2011:92‐8. [ISBN 978‐5‐9704‐1893‐2]
Ivashkin 2011b
-
- Ivashkin VT, Pavlov CS. Liver biopsy and morphological investigation of chronic liver disease. In: Ivashkin VT, Pavlov CS editor(s). Liver Fibrosis. Moscow: Geotar‐Media, 2011:13‐22. [ISBN 978‐5‐9704‐1893‐2]
Iyo 2009
-
- Iyo AY. Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging: a literature review. Journal of Diagnostic Medical Sonography 2009;25(4):204‐11.
Jaurigue 2014
Jüni 1999
-
- Jüni P, Witschi A, Bloch R, Egger M. The hazards of scoring the quality of clinical trials for meta‐analysis. JAMA 1999;282(11):1054‐60. - PubMed
Kleiner 2005
-
- Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Natta M, Behling C, Contos MJ, Cummings OW, Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Clinical Research Network. Design and validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 2005;41(6):1313‐21. - PubMed
Knodell 1981
-
- Knodell RG, Ishak KG, Black WC, Chen TS, Craig R, Kaplowitz N, et al. Formulation and application of a numerical scoring system for assessing histological activity in asymptomatic chronic active hepatitis. Hepatology 1981;1(5):431‐5. - PubMed
Kuntz 2008
-
- Kuntz E, Kuntz H‐D. Hepatology. 3rd Edition. Heidelberg: Springer Medizin Verlag, 2008.
Leone 2010
Leong 2012
-
- Leong J, Im GY. Evaluation and selection of the patient with alcoholic liver disease for liver transplant. Clinical Liver Disease 2012;16(4):851‐63. - PubMed
Lijmer 1999
-
- Lijmer JG, Mol BW, Heisterkamp S, Bonsel GJ, Prins MH, Meulen JH, et al. Empirical evidence of design‐related bias in studies of diagnostic tests. JAMA 1999;282(11):1061‐6. - PubMed
Liu 2012
Liu 2013
Macaskill 2010
-
- Macaskill P, Gatsonis C, Deeks JJ, Harbord RM, Takwoingi Y. Chapter 10: Analysing and presenting results. In: Deeks JJ, Bossuyt PM, Gatsonis C (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Diagnostic Test Accuracy Version 1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2010. Available from srdta.cochrane.org/.
MacSween 1986
-
- MacSween RN, Burt AD. Histologic spectrum of alcoholic liver disease. Seminars in Liver Disease 1986;6:221‐32. - PubMed
Michalak 2003
-
- Michalak S, Rousselet M‐C, Bedossa P, Pilette C, Chappard D, Oberti F, et al. Respective roles of portoseptal fibrosis and centrilobular fibrosis in alcoholic liver disease. Journal of Pathology 2003;201(1):55‐62. - PubMed
Minozzi 2010
Morra 2007
-
- Morra R, Munteanu M, Imbert‐Bismut F, Messous D, Ratziu V, Poynard T. FibroMAX: towards a new universal biomarker of liver disease?. Expert Review of Molecular Diagnostics 2007;7(5):481‐90. - PubMed
Naveau 1997
-
- Naveau S, Giraud V, Borotto E, Aubert A, Capron F, Chaput JC. Excess weight risk factor for alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology 1997;25(1):108‐11. - PubMed
Nishiura 2005
-
- Nishiura T, Watanabe H, Ito M, Matsuoka Y, Yano K, Daikoku M, et al. Ultrasound evaluation of the fibrosis stage in chronic liver disease by the simultaneous use of low and high frequency probes. British Journal of Radiology 2005;78:189‐97. - PubMed
O'Shea 2010
-
- O'Shea RS, Dasarathy S, McCullough AJ, the Practice Guideline Committee of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology. Alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology 2010;51(1):307‐28. - PubMed
Pani 2014
Pavlov 2015
-
- Pavlov CS, Casazza G, Nikolova D, Tsochatzis E, Burroughs AK, Ivashkin VT, et al. Transient elastography for diagnosis of stages of hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis in people with alcoholic liver disease. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015, Issue 1. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD010542] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Poulsen 1979
-
- Poulsen HE, Christoffersen P. Atlas of Liver Biopsies. Copenhagen: Munksgaard, 1979.
Poynard 2007
Poynard 2008
Regev 2002
-
- Regev A, Berho M, Jeffers LJ, Milikowski C, Molina EG, Pyrsopoulos NT, et al. Sampling error and intraobserver variation in liver biopsy in patients with chronic HCV infection. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2002;97(10):2614‐8. - PubMed
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Rocco 2014
Rockey 2009
-
- Rockey DC, Caldwell SH, Goodman ZD, Nelson RC, Smith AD. Liver biopsy. Hepatology 2009;49(3):1017‐44. - PubMed
Rutjes 2006
Rösner 2010a
Rösner 2010b
Savolainen 1993
-
- Savolainen VT, Liesto K, Männikkö A, Penttilä A, Karhunen PJ. Alcohol consumption and alcoholic liver disease: evidence of a threshold level of effects of ethanol. Alcoholism, Clinical and Experimental Research 1993;17:1112‐7. - PubMed
Schoenfeld 1999
-
- Schoenfeld P, Guyatt G, Hamilton F, Laine L, Cook D, Bjorkman D, et al. An evidence‐based approach to gastroenterology diagnosis. Gastroenterology 1999;116:1230‐7. - PubMed
Schuetz 2012
Seeff 2010
Sherlock 1997
-
- Sherlock S, Dooley J. Alcohol and the liver. Diseases of the Liver and Biliary System. 10th Edition. London: Blackwell Science, 1997:385‐403.
Shiha 2009
Singal 2013
Smidt 2005
-
- Smidt N, Rutjes AW, Windt DA, Ostelo RW, Reitsma JB, Bossuyt PM, et al. Quality of reporting of diagnostic accuracy studies. Radiology 2005;235:347‐53. - PubMed
Stewart 2001
-
- Stewart S, Jones D, Day CP. Alcoholic liver disease: new insights into mechanisms and preventative strategies. Trends in Molecular Medicine 2001;7(9):408‐13. - PubMed
Testino 2014
Verrill 2009
-
- Verrill C, Markham H, Templeton A, Carr NJ, Sheron N. Alcohol‐related cirrhosis ‐ early abstinence is a key factor in prognosis, even in the most severe cases. Addiction 2009;104:768‐74. - PubMed
Whiting 2004
-
- Whiting P, Rutjes AW, Reitsma JB, Glas AS, Bossuyt PM, Kleijnen J. Sources of variation and bias in studies of diagnostic accuracy: a systematic review. Annals of Internal Medicine 2004;140(3):189‐202. - PubMed
Whiting 2005
Whiting 2011
-
- Whiting PF, Weswood ME, Rutjes AW, Reitsma JB, Bossuyt PN, Kleijnen J. QUADAS‐2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Annals of Internal Medicine 2011;155:529‐36. - PubMed
WHO 2010
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Global strategy to reduce the harmful use of alcohol, 2010. www.who.int/substance_abuse/alcstratenglishfinal.pdf (accessed 16 March 2015).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

