Preferential targeting of cancer stem cells in the radiosensitizing effect of ABT-737 on HNSCC
- PMID: 26934442
- PMCID: PMC4941347
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.7744
Preferential targeting of cancer stem cells in the radiosensitizing effect of ABT-737 on HNSCC
Abstract
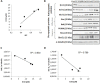
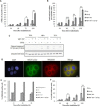
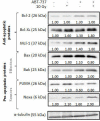
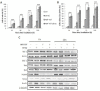
Head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCC) are common human malignancies with poor clinical outcomes. The 5-year survival rates for patients with advanced stage HNSCC have not changed appreciably in the past few decades, underscoring a dire need for improved therapeutic options. HNSCC is frequently characterized by overexpression of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members. Increased levels of these anti-apoptotic proteins have been associated with radio- and chemoresistance and poor clinical outcome. The aim of this study was to evaluate combined effects of radiation and ABT-737, a BH3-mimetic molecule, in HNSCC. Although ABT-737, as a single agent, was largely ineffective at promoting HNSCC cell death, we found that combining ABT-737 and radiation induced strong synergistic apoptosis in HNSCC cell lines and delayed tumoral growth in vivo. Moreover, we demonstrated for the first time that ABT-737, alone or in combination with radiation, can efficiently eliminate cancer stem cells (CSCs). Altogether, our results indicate that therapy targeting anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members could be a highly effective potential adjuvant to radiotherapy capable of targeting CSCs in HNSCC and therefore overcoming cancer recurrence and metastasis.
Keywords: ABT-737; Bcl-2 family; cancer stem cells; head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; radiation.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Combining radiation to EGFR and Bcl-2 blockade: a new approach to target cancer stem cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021 Jul;147(7):1905-1916. doi: 10.1007/s00432-021-03593-8. Epub 2021 Mar 31. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33791846 Free PMC article.
-
ABT-737 synergizes with chemotherapy to kill head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells via a Noxa-mediated pathway.Mol Pharmacol. 2009 May;75(5):1231-9. doi: 10.1124/mol.108.052969. Epub 2009 Feb 25. Mol Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19246337 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Bcl-2 potentiates AZD-2014-induced anti-head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell activity.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Sep 2;477(4):607-613. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.06.100. Epub 2016 Jun 22. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 27343560
-
Targeting proliferation and survival pathways in head and neck cancer for therapeutic benefit.Chin J Cancer. 2012 Jul;31(7):319-26. doi: 10.5732/cjc.011.10404. Epub 2012 Jan 17. Chin J Cancer. 2012. PMID: 22257382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of non-coding RNAs as potential targets in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cancer stem cells.Curr Drug Targets. 2014;15(13):1247-60. doi: 10.2174/1389450115666141024113446. Curr Drug Targets. 2014. PMID: 25341422 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigallocatechin gallate and curcumin inhibit Bcl-2: a pharmacophore and docking based approach against cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2024 Jul 8;26(1):114. doi: 10.1186/s13058-024-01868-9. Breast Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38978121 Free PMC article.
-
Combining radiation to EGFR and Bcl-2 blockade: a new approach to target cancer stem cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021 Jul;147(7):1905-1916. doi: 10.1007/s00432-021-03593-8. Epub 2021 Mar 31. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33791846 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting stem cells by radiation: From the biological angle to clinical aspects.World J Stem Cells. 2016 Aug 26;8(8):243-50. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v8.i8.243. World J Stem Cells. 2016. PMID: 27621758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
B Cell Lymphoma 2: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Cancer Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 28;22(19):10442. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910442. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638779 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The elevated activation of NFκB and AP-1 is correlated with differential regulation of Bcl-2 and associated with oral squamous cell carcinoma progression and resistance.Clin Oral Investig. 2017 Dec;21(9):2721-2731. doi: 10.1007/s00784-017-2074-6. Epub 2017 Feb 23. Clin Oral Investig. 2017. PMID: 28233171
References
-
- Clark J, Li W, Smith G, Shannon K, Clifford A, McNeil E, Gao K, Jackson M, Mo Tin M, O‘Brien C. Outcome of treatment for advanced cervical metastatic squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck. 2005;27:87–94. - PubMed
-
- Trask DK, Wolf GT, Bradford CR, Fisher SG, Devaney K, Johnson M, Singleton T, Wicha M. Expression of Bcl-2 family proteins in advanced laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma: correlation with response to chemotherapy and organ preservation. Laryngoscope. 2002;112:638–644. - PubMed
-
- Pena JC, Thompson CB, Recant W, Vokes EE, Rudin CM. Bcl-xL and Bcl-2 expression in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Cancer. 1999;85:164–170. - PubMed
-
- Homma A, Furuta Y, Oridate N, Nakano Y, Kohashi G, Yagi K, Nagahashi T, Yagi K, Nagahashi T, Fukuda S, Inoue K, Inuyama Y. Prognostic significance of clinical parameters and biological markers in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck treated with concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 1995;5:801–806. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

