Development of a specific affinity-matured exosite inhibitor to MT1-MMP that efficiently inhibits tumor cell invasion in vitro and metastasis in vivo
- PMID: 26934448
- PMCID: PMC4941350
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.7780
Development of a specific affinity-matured exosite inhibitor to MT1-MMP that efficiently inhibits tumor cell invasion in vitro and metastasis in vivo
Abstract
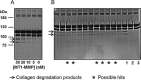
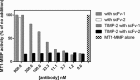
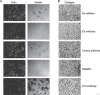
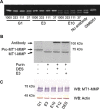
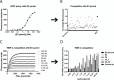
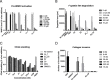
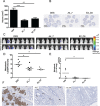
The membrane-associated matrix metalloproteinase-14, MT1-MMP, has been implicated in pericellular proteolysis with an important role in cellular invasion of collagenous tissues. It is substantially upregulated in various cancers and rheumatoid arthritis, and has been considered as a potential therapeutic target. Here, we report the identification of antibody fragments to MT1-MMP that potently and specifically inhibit its cell surface functions. Lead antibody clones displayed inhibitory activity towards pro-MMP-2 activation, collagen-film degradation and gelatin-film degradation, and were shown to bind to the MT1-MMP catalytic domain outside the active site cleft, inhibiting binding to triple helical collagen. Affinity maturation using CDR3 randomization created a second generation of antibody fragments with dissociation constants down to 0.11 nM, corresponding to an improved affinity of 332-fold with the ability to interfere with cell-surface MT1-MMP functions, displaying IC50 values down to 5 nM. Importantly, the new inhibitors were able to inhibit collagen invasion by tumor-cells in vitro and in vivo primary tumor growth and metastasis of MDA-MB-231 cells in a mouse orthotopic xenograft model. Herein is the first demonstration that an inhibitory antibody targeting sites outside the catalytic cleft of MT1-MMP can effectively abrogate its in vivo activity during tumorigenesis and metastasis.
Keywords: MT1-MMP; antibody; in vivo targeting; metastasis; non-catalytic sites.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interests.
Figures
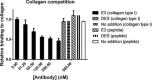
Similar articles
-
Selective function-blocking monoclonal human antibody highlights the important role of membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) in metastasis.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 10;8(2):2781-2799. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13157. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27835863 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of MT1-MMP activity using functional antibody fragments selected against its hemopexin domain.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012 Feb;44(2):393-403. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2011.11.015. Epub 2011 Nov 26. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22138224
-
MT-LOOP-dependent localization of membrane type I matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) to the cell adhesion complexes promotes cancer cell invasion.J Biol Chem. 2013 Dec 6;288(49):35126-37. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.496067. Epub 2013 Oct 28. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24165131 Free PMC article.
-
Coordinate action of membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MT1-MMP) and MMP-2 enhances pericellular proteolysis and invasion.Cancer Sci. 2010 Apr;101(4):843-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01498.x. Epub 2010 Jan 18. Cancer Sci. 2010. PMID: 20148894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Matrix invasion by tumour cells: a focus on MT1-MMP trafficking to invadopodia.J Cell Sci. 2009 Sep 1;122(Pt 17):3015-24. doi: 10.1242/jcs.034561. J Cell Sci. 2009. PMID: 19692588 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Potential of Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibition in Breast Cancer.J Cell Biochem. 2017 Nov;118(11):3531-3548. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26185. Epub 2017 Jul 17. J Cell Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28585723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Monoclonal antibodies against metzincin targets.Br J Pharmacol. 2019 Jan;176(1):52-66. doi: 10.1111/bph.14186. Epub 2018 Apr 2. Br J Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 29488211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Riding the metalloproteinase roller coaster.J Biol Chem. 2017 May 12;292(19):7708-7718. doi: 10.1074/jbc.X117.785295. Epub 2017 Mar 15. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28298437 Free PMC article.
-
The Rebirth of Matrix Metalloproteinase Inhibitors: Moving Beyond the Dogma.Cells. 2019 Aug 27;8(9):984. doi: 10.3390/cells8090984. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31461880 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Active-site MMP-selective antibody inhibitors discovered from convex paratope synthetic libraries.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Dec 27;113(52):14970-14975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1609375114. Epub 2016 Dec 13. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27965386 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Itoh Y, Seiki M. MT1-MMP: a potent modifier of pericellular microenvironment. J Cell Physiol. 2006;206:1–8. - PubMed
-
- Knauper V, Will H, Lopez-Otin C, Smith B, Atkinson SJ, Stanton H, Hembry RM, Murphy G. Cellular mechanisms for human procollagenase-3 (MMP-13) activation. Evidence that MT1-MMP (MMP-14) and gelatinase a (MMP-2) are able to generate active enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:17124–17131. - PubMed
-
- Will H, Atkinson SJ, Butler GS, Smith B, Murphy G. The soluble catalytic domain of membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase cleaves the propeptide of progelatinase A and initiates autoproteolytic activation. Regulation by TIMP-2 and TIMP-3. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:17119–17123. - PubMed
-
- Holopainen JM, Moilanen JA, Sorsa T, Kivela-Rajamaki M, Tervahartiala T, Vesaluoma MH, Tervo TM. Activation of matrix metalloproteinase-8 by membrane type 1-MMP and their expression in human tears after photorefractive keratectomy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003;44:2550–2556. - PubMed
-
- Pavlaki M, Zucker S. Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors (MMPIs): the beginning of phase I or the termination of phase III clinical trials. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003;22:177–203. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

