Randomized clinical trial on 7-days-a-week post-operative radiotherapy vs concurrent post-operative radiochemotherapy in locally advanced cancer of the oral cavity/oropharynx: a report on acute normal tissue reactions
- PMID: 26934504
- PMCID: PMC4985452
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20150805
Randomized clinical trial on 7-days-a-week post-operative radiotherapy vs concurrent post-operative radiochemotherapy in locally advanced cancer of the oral cavity/oropharynx: a report on acute normal tissue reactions
Abstract
Objective: The purpose of the study was to evaluate acute normal tissue reactions and treatment compliance in a randomized clinical trial on 7-days-a-week post-operative radiotherapy (p-CAIR) vs post-operative concurrent radiochemotherapy (p-RTCT) in locally advanced cancer of the oral cavity/oropharynx. The sample analyzed at present represents approximately 30% of the intended future trial size.
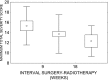
Methods: The patients were randomly assigned to receive 63 Gy in 1.8-Gy fractions 7 days a week (n = 44) or 63 Gy in 1.8-Gy fractions 5 days a week with concurrent cisplatin 80-100 mg per square metre of body surface area on Days 1, 22 and 43 of the course of radiotherapy (n = 40). Acute mucosal reactions were scored using the modified Dische system.
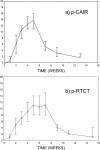
Results: 15 (17.9%) patients, including 5 patients in p-CAIR and 10 patients in p-RTCT, did not comply with the assigned radiation treatment, mostly because of rapid tumour progression or deteriorating general performance. In p-RTCT, 22 (55%) patients received less than the intended three courses of chemotherapy mostly owing to haematological toxicity. The average maximum mucosal severity score was 14.2 in p-CAIR compared with 13.4 in p-RTCT; the difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.31).
Conclusion: The schedules compared (p-CAIR and p-RTCT) did not differ considerably with respect to acute mucosal reactions. Haematological toxicity in p-RTCT was elevated compared with p-CAIR. Both schedules were considered tolerable with respect to acute toxicity, which justifies further recruitment to the trial.
Advances in knowledge: The results show that early mucosal reactions are comparable in both trial arms but haematological toxicity is more pronounced during radiochemotherapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Randomised clinical trial on 7-days-a-week postoperative radiotherapy vs. concurrent postoperative radio-chemotherapy in locally advanced cancer of the oral cavity/oropharynx.Br J Radiol. 2020 Dec 1;93(1116):20200288. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20200288. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Br J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32960662 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Randomized clinical trial on continuous 7-days-a-week postoperative radiotherapy for high-risk squamous cell head-and-neck cancer: a report on acute normal tissue reactions.Radiother Oncol. 2005 Oct;77(1):58-64. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2005.07.007. Epub 2005 Sep 12. Radiother Oncol. 2005. PMID: 16157401 Clinical Trial.
-
Randomized clinical trial on 7-days-a-week postoperative radiotherapy for high-risk squamous cell head and neck cancer.Radiother Oncol. 2008 May;87(2):155-63. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2008.02.009. Epub 2008 Mar 14. Radiother Oncol. 2008. PMID: 18342964 Clinical Trial.
-
Do acute mucosal reactions lead to consequential late reactions in patients with head and neck cancer?Radiother Oncol. 1999 Aug;52(2):157-64. doi: 10.1016/s0167-8140(99)00107-3. Radiother Oncol. 1999. PMID: 10577701 Clinical Trial.
-
Randomized clinical trial on 7-day-continuous accelerated irradiation (CAIR) of head and neck cancer - report on 3-year tumour control and normal tissue toxicity.Radiother Oncol. 2000 May;55(2):101-10. doi: 10.1016/s0167-8140(00)00139-0. Radiother Oncol. 2000. PMID: 10799721 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Randomised clinical trial on 7-days-a-week postoperative radiotherapy vs. concurrent postoperative radio-chemotherapy in locally advanced cancer of the oral cavity/oropharynx.Br J Radiol. 2020 Dec 1;93(1116):20200288. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20200288. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Br J Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32960662 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Suwinski R, Sowa A, Rutkowski T, Wydmanski J, Tarnawski R, Maciejewski B. Time factor in postoperative radiotherapy: a multivariate locoregional control analysis in 868 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2003; 56: 399–412. - PubMed
-
- Awwad HK, Lotayef M, Shouman T, Begg AC, Wilson G, Bentzen SM, et al. . Accelerated hyperfractionation (AHF) compared to conventional fractionation (CF) in the postoperative radiotherapy of locally advanced head and neck cancer: influence of proliferation. Br J Cancer 2002; 86: 517–23. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6600119 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

