Inhibition of IRE1α-driven pro-survival pathways is a promising therapeutic application in acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 26934650
- PMCID: PMC4951325
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.7702
Inhibition of IRE1α-driven pro-survival pathways is a promising therapeutic application in acute myeloid leukemia
Erratum in
-
Correction: Inhibition of IRE1α-driven pro-survival pathways is a promising therapeutic application in acute myeloid leukemia.Oncotarget. 2017 Sep 8;8(38):64651. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20707. eCollection 2017 Sep 8. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28969101 Free PMC article.
Abstract
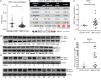
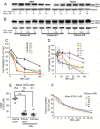
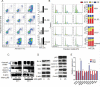
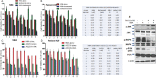
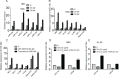
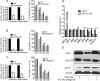
Survival of cancer cells relies on the unfolded protein response (UPR) to resist stress triggered by the accumulation of misfolded proteins within the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The IRE1α-XBP1 pathway, a key branch of the UPR, is activated in many cancers. Here, we show that the expression of both mature and spliced forms of XBP1 (XBP1s) is up-regulated in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cell lines and AML patient samples. IRE1α RNase inhibitors [MKC-3946, 2-hydroxy-1-naphthaldehyde (HNA), STF-083010 and toyocamycin] blocked XBP1 mRNA splicing and exhibited cytotoxicity against AML cells. IRE1α inhibition induced caspase-dependent apoptosis and G1 cell cycle arrest at least partially by regulation of Bcl-2 family proteins, G1 phase controlling proteins (p21cip1, p27kip1 and cyclin D1), as well as chaperone proteins. Xbp1 deleted murine bone marrow cells were resistant to growth inhibition by IRE1α inhibitors. Combination of HNA with either bortezomib or AS2O3 was synergistic in AML cytotoxicity associated with induction of p-JNK and reduction of p-PI3K and p-MAPK. Inhibition of IRE1α RNase activity increased expression of many miRs in AML cells including miR-34a. Inhibition of miR-34a conferred cellular resistance to HNA. Our results strongly suggest that targeting IRE1α driven pro-survival pathways represent an exciting therapeutic approach for the treatment of AML.
Keywords: ER stress; IRE1; XBP1; micro RNA; unfolded protein response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest
Figures

References
-
- Lowenberg B, Downing JR, Burnett A. Acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:1051–1062. - PubMed
-
- Giles FJ, Keating A, Goldstone AH, Avivi I, Willman CL, Kantarjian HM. Acute myeloid leukemia. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2002:73–110. - PubMed
-
- Bonnet D, Dick JE. Human acute myeloid leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a primitive hematopoietic cell. Nat Med. 1997;3:730–737. - PubMed
-
- Chan WI, Huntly BJ. Leukemia stem cells in acute myeloid leukemia. Semin Oncol. 2008;35:326–335. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

