In vitro model of bone to facilitate measurement of adhesion forces and super-resolution imaging of osteoclasts
- PMID: 26935172
- PMCID: PMC4776281
- DOI: 10.1038/srep22585
In vitro model of bone to facilitate measurement of adhesion forces and super-resolution imaging of osteoclasts
Abstract
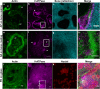
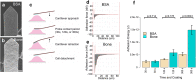
To elucidate processes in the osteoclastic bone resorption, visualise resorption and related actin reorganisation, a combination of imaging technologies and an applicable in vitro model is needed. Nanosized bone powder from matching species is deposited on any biocompatible surface in order to form a thin, translucent, smooth and elastic representation of injured bone. Osteoclasts cultured on the layer expressed matching morphology to ones cultured on sawed cortical bone slices. Resorption pits were easily identified by reflectance microscopy. The coating allowed actin structures on the bone interface to be visualised with super-resolution microscopy along with a detailed interlinked actin networks and actin branching in conjunction with V-ATPase, dynamin and Arp2/3 at actin patches. Furthermore, we measured the timescale of an adaptive osteoclast adhesion to bone by force spectroscopy experiments on live osteoclasts with bone-coated AFM cantilevers. Utilising the in vitro model and the advanced imaging technologies we localised immunofluorescence signals in respect to bone with high precision and detected resorption at its early stages. Put together, our data supports a cyclic model for resorption in human osteoclasts.
Figures






Similar articles
-
p130Cas, Crk-associated substrate, plays important roles in osteoclastic bone resorption.J Bone Miner Res. 2013 Dec;28(12):2449-62. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.1936. J Bone Miner Res. 2013. PMID: 23526406
-
Human osteoclasts, not osteoblasts, deposit osteopontin onto resorption surfaces: an in vitro and ex vivo study of remodeling bone.J Bone Miner Res. 1995 Nov;10(11):1666-80. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650101109. J Bone Miner Res. 1995. PMID: 8592943
-
Scanning electrochemical microscopy at the surface of bone-resorbing osteoclasts: evidence for steady-state disposal and intracellular functional compartmentalization of calcium.J Bone Miner Res. 2001 Nov;16(11):2092-102. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.2001.16.11.2092. J Bone Miner Res. 2001. PMID: 11697806
-
Atomic force microscopy of collagen structure in bone and dentine revealed by osteoclastic resorption.Ultramicroscopy. 2005 Nov;105(1-4):79-89. doi: 10.1016/j.ultramic.2005.06.021. Epub 2005 Aug 8. Ultramicroscopy. 2005. PMID: 16125320
-
Podosome and sealing zone: specificity of the osteoclast model.Eur J Cell Biol. 2006 Apr;85(3-4):195-202. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2005.09.008. Epub 2005 Oct 24. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16546562 Review.
Cited by
-
Cell Sources for Human In vitro Bone Models.Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2021 Feb;19(1):88-100. doi: 10.1007/s11914-020-00648-6. Epub 2021 Jan 15. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2021. PMID: 33447910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of minor amounts of β-calcium pyrophosphate and hydroxyapatite on the physico-chemical properties and osteoclastic resorption of β-tricalcium phosphate cylinders.Bioact Mater. 2021 Sep 23;10:222-235. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2021.09.003. eCollection 2022 Apr. Bioact Mater. 2021. PMID: 34901541 Free PMC article.
-
Diversity of actin architecture in human osteoclasts: network of curved and branched actin supporting cell shape and intercellular micrometer-level tubes.Mol Cell Biochem. 2017 Aug;432(1-2):131-139. doi: 10.1007/s11010-017-3004-2. Epub 2017 Mar 14. Mol Cell Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28293874 Free PMC article.
-
Cimetidine-induced androgenic failure causes cell death and changes in actin, EGF and V-ATPase immunoexpression in rat submandibular glands.J Anat. 2021 Jul;239(1):136-150. doi: 10.1111/joa.13408. Epub 2021 Mar 13. J Anat. 2021. PMID: 33713423 Free PMC article.
-
Surface microtopography modulates sealing zone development in osteoclasts cultured on bone.J R Soc Interface. 2017 Feb;14(127):20160958. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2016.0958. J R Soc Interface. 2017. PMID: 28202594 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kleinhans C., Schmid F. F., Schmid F. V. & Kluger P. J. Comparison of osteoclastogenesis and resorption activity of human osteoclasts on tissue culture polystyrene and on natural extracellular bone matrix in 2D and 3D. Journal of Biotechnology 205, 101–110 (2015). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

