Chest wall desmoid tumours treated with definitive radiotherapy: a plan comparison of 3D conformal radiotherapy, intensity-modulated radiotherapy and volumetric-modulated arc radiotherapy
- PMID: 26935470
- PMCID: PMC4776360
- DOI: 10.1186/s13014-016-0611-0
Chest wall desmoid tumours treated with definitive radiotherapy: a plan comparison of 3D conformal radiotherapy, intensity-modulated radiotherapy and volumetric-modulated arc radiotherapy
Abstract
Purpose: Definitive radiotherapy is often used for chest wall desmoid tumours due to size or anatomical location. The delivery of radiotherapy is challenging due to the large size and constraints of normal surrounding structures. We compared the dosimetry of 3D conformal radiotherapy (3DCRT), intensity-modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) and volumetric-modulated arc radiotherapy (VMAT) to evaluate the best treatment option.
Methods and materials: Ten consecutive patients with inoperable chest wall desmoid tumours (PTV range 416-4549 cm(3)) were selected. For each patient, 3DCRT, IMRT and VMAT plans were generated and the Conformity Index (CI), organ at risk (OAR) doses and monitor unit (MU) were evaluated. The Wilcoxon signed-rank test was used to compare dose delivered to both target and OARs.
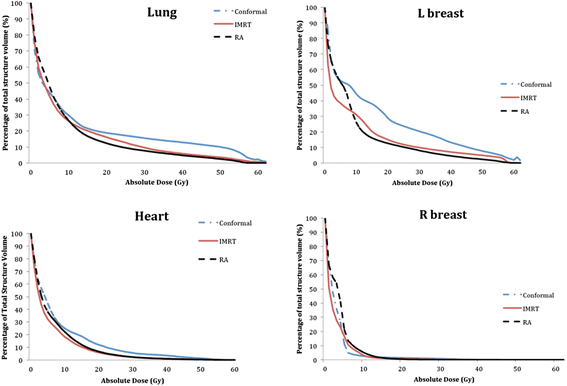
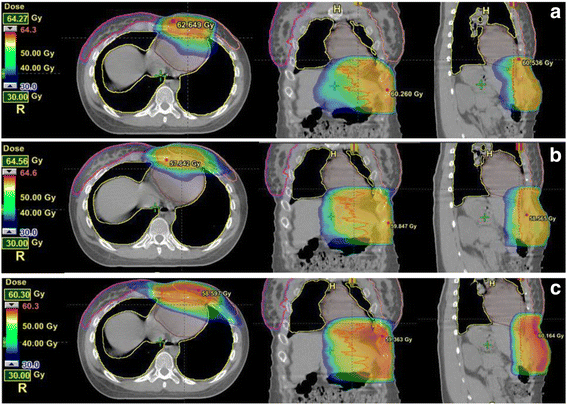
Results: The mean number of fields for 3DCRT and IMRT were 6.3 ± 2.1, 7.2 ± 1.8. The mean number of arcs for VMAT was 3.7 ± 1.1. The mean conformity index of VMAT (0.98 ± 0.14) was similar to that of IMRT (1.03 ± 0.13), both of which were significantly better than 3DCRT (1.35 ± 0.20; p = 0.005). The mean dose to lung was significantly higher for 3DCRT (11.9Gy ± 7.9) compared to IMRT (9.4Gy ± 5.4, p = 0.014) and VMAT (8.9Gy ± 4.5, p = 0.017). For the 3 females, the low dose regions in the ipsilateral breast for VMAT were generally less with VMAT. IMRT plans required 1427 ± 532 MU per fraction which was almost 4-fold higher than 3DCRT (313 ± 112, P = 0.005). Compared to IMRT, VMAT plans required 60 % less MU (570 ± 285, P = 0.005).
Conclusions: For inoperable chest wall desmoid tumours, VMAT delivered equivalent target coverage when compared to IMRT but required 60 % less MU. Both VMAT and IMRT were superior to 3DCRT in terms of better PTV coverage and sparing of lung tissue.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Radiation therapy of synchronous bilateral breast carcinoma (SBBC) using multiple techniques.Med Dosim. 2018 Spring;43(1):55-68. doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2017.08.003. Epub 2017 Oct 5. Med Dosim. 2018. PMID: 28988893
-
Treatment of left sided breast cancer for a patient with funnel chest: volumetric-modulated arc therapy vs. 3D-CRT and intensity-modulated radiotherapy.Med Dosim. 2013 Spring;38(1):1-4. doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2012.04.003. Epub 2012 Jun 22. Med Dosim. 2013. PMID: 22727550
-
The Effect of Flattening Filter Free on Three-dimensional Conformal Radiation Therapy (3D-CRT), Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT), and Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT) Plans for Metastatic Brain Tumors from Non-small Cell Lung Cancer.Health Phys. 2015 Jul;109(1):1-9. doi: 10.1097/HP.0000000000000278. Health Phys. 2015. PMID: 26011493
-
Hybrid Treatment Planning for Chest Wall Irradiation Utilizing Three-Dimensional Conformal Radiotherapy (3DCRT), Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT), and Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT): A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2024 May 3;16(5):e59583. doi: 10.7759/cureus.59583. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38832195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Robust optimization in lung treatment plans accounting for geometric uncertainty.J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2018 May;19(3):19-26. doi: 10.1002/acm2.12291. Epub 2018 Mar 10. J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2018. PMID: 29524301 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proton Therapy in Non-Rhabdomyosarcoma Soft Tissue Sarcomas of Children and Adolescents.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Apr 26;16(9):1694. doi: 10.3390/cancers16091694. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38730646 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dosimetric study of TrueBeam single-isocenter vs. Halcyon dual-isocenter VMAT radiotherapy plans for postoperative left-sided breast cancer.BMC Cancer. 2025 Jul 25;25(1):1214. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14574-2. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40713575 Free PMC article.
-
Significant symptoms alleviation and tumor volume reduction after combined simultaneously integrated inner-escalated boost and volumetric-modulated arc radiotherapy in a patient with unresectable bulky hepatocellular carcinoma: A care-compliant case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Aug;95(34):e4717. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000004717. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27559982 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Tumors of the Breast: Fibroblastic/Myofibroblastic Lesions and Other Lesions.Curr Oncol. 2023 Apr 24;30(5):4437-4482. doi: 10.3390/curroncol30050338. Curr Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37232796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dosimetric analysis of half-field-based VMAT with the deep inspiration breath-hold technique for left breast cancer patients following breast-conserving surgery.Front Oncol. 2024 Nov 21;14:1418723. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1418723. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39640275 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fletcher J, Bridge J, Hogendoorn P. Desmoid-type fibromatoses. WHO Classification of Tumors of Soft Tissue and Bone. Lyon: IARC Press; 2013. pp. 72–3.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials