Blood pressure lowering efficacy of coenzyme Q10 for primary hypertension
- PMID: 26935713
- PMCID: PMC6486033
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD007435.pub3
Blood pressure lowering efficacy of coenzyme Q10 for primary hypertension
Abstract
Background: Blood pressure is a commonly measured risk factor for non-fatal and fatal cardiovascular adverse events such as heart attacks and strokes. Clinical trials have suggested that coenzyme Q10, a non-prescription nutritional supplement, can effectively lower blood pressure (BP). When this review was completed and published in October 2009, it concluded that "due to the possible unreliability of the 3 included studies, it is uncertain whether or not coenzyme Q10 reduces blood pressure in the long-term management of primary hypertension."
Objectives: To determine the blood pressure lowering effect of coenzyme Q10 in primary hypertension.
Search methods: We searched the Hypertension Group Specialised Register (1946 to November 2015), The Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (The Cochrane Library 2015, Issue 10), MEDLINE (1946 to November 2015), MEDLINE In-Process (accessed 10 November 2015), EMBASE (1974 to November 2015), Web of Science (1899 to November 2015), CINAHL (1970 to November 2015), and ClinicalTrials.gov (accessed 10 November 2015). We also searched reference lists of articles for relevant clinical trials in any language.
Selection criteria: Double blind, randomized, placebo-controlled parallel or cross-over trials evaluating the blood pressure (BP) lowering efficacy of coenzyme Q10 for a duration of at least three weeks, in patients with primary hypertension.
Data collection and analysis: The primary author determined trial inclusion, extracted the data and assessed the risk of bias. The second author independently verified trial inclusion and data extraction.
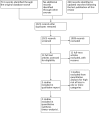
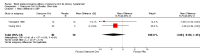
Main results: In this update of the review, one new randomized, controlled cross-over trial with a total of 30 participants was added, and one trial included in the initial review was excluded. Only two of the three included trials were pooled in the meta-analysis, as one trial was judged to have an unacceptably high risk of bias. In the meta-analysis of two RCTs (50 participants), coenzyme Q10 did not significantly change systolic BP: -3.68 mm Hg (95% confidence interval (CI) -8.86 to 1.49), or diastolic BP: -2.03 mm Hg (95% CI -4.86 to 0.81] ), based on clinic data.
Authors' conclusions: This review provides moderate-quality evidence that coenzyme Q10 does not have a clinically significant effect on blood pressure. In one of three trials reporting adverse effects, coenzyme Q10 was well tolerated. Due to the small number of individuals and studies available for analysis, more well-conducted trials are needed.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures





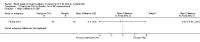


Update of
-
Blood pressure lowering efficacy of coenzyme Q10 for primary hypertension.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009 Oct 7;(4):CD007435. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007435.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Mar 03;3:CD007435. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007435.pub3. PMID: 19821418 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Digiesi 1990 {published data only}
-
- Digiesi V, Cantini F, Brodbeck B. Effect of coenzyme Q10 on essential arterial hypertension. Current Therapeutic Research May 1990;47:841‐5.
Yamagami 1986 {published data only}
-
- Yamagami T, Takagt M, Akagami H, Kubo H, Toyama S, Okamoto T, et al. Effect of coenzyme Q10 on essential hypertension, a double blind controlled study. Biomedical and Clinical Aspects of Coenzyme Q 1986;5:337‐43.
Young 2012 {published data only}
-
- Young JM, Florkowski CM, Molyneux SL, McEwan RG, Frampton CM, Nicholls MG, et al. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled crossover study of Coenzyme Q10 therapy in hypertensive patients with the metabolic syndrome. American Journal of Hypertension Feb 2012;25(2):261‐270. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Burke 2001 {published data only}
-
- Burke BE, Neuenschwander R, Olson RD. Randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial of Coenzyme Q10 in isolated systolic hypertension. Southern Medical Journal 2001;94(11):1112‐7. - PubMed
Digiesi 1994 {published data only}
-
- Digiesi V, Cantini F, Oradei A, Bisi G, Guarino GC, Brocchi A, et al. Coenzyme Q10 in essential hypertension. Molecular Aspects of Medicine 1994;15 Suppl:s257‐63. - PubMed
Drzewoski 1981 {published data only}
-
- Drzewoski J, Folkers K, Richardson PC, Shizukuishi S, Baker LE. Usefulness of coenzyme Q10 in the treatment of hypertension. Polski Tygodnik Lekarski 1981;36(27):997‐1001. - PubMed
Eghtesadi 2012 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Eghtesadi S, Jazayeri S, Rezai N, Heidari I, Shidfar F, Haghighi H. Study of the effect of CoQ10 on paraoxonase activity, total antioxidant capacity, malondialdehyde, HSCRP, LIPID profile and glycemic control in type 2 diabetic patients. 19th European Congress on Obesity, ECO2012 2012;5:129.
Folkers 1981 {published data only}
-
- Folkers K, Drzewoski J, Richardson PC, Ellis J, Shizukuishi S, Baker L. Bioenergetics in clinical medicine. XVI. Reduction of hypertension in patients by therapy with coenzyme Q10. Res Comm Chem Pathol Pharmacol 1981;31(1):129‐40. - PubMed
Hata 1977 {published data only}
-
- Hata S, Kunida H, Oyama Y. Antihypertensive effects of coenzyme Q10 in essential hypertension ‐ in relation to the renin‐aldosterone system. Horumon to Rinsho ‐ Clinical Endocrinology 1977;25(9):1019‐23. - PubMed
Hodgson 2002 {published data only}
-
- Hodgson JM, Watts GF, Playford DA, Burke V, Croft KD. Coenzyme Q10 improves blood pressure and glycaemic control: a controlled trial in subjects with type 2 diabetes. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2002;56:1137‐42. - PubMed
Langsjoen 1994 {published data only}
-
- Langsjoen P, Willis R, Folkers K. Treatment of essential hypertension with coenzyme Q10. Molecular Aspects of Medicine 1994;15 Suppl:S265‐72. - PubMed
Shah 2007 {published data only}
-
- Shah SA, Sander S, Cios D, Lipeika J, Kluger J, White CM. Electrocardiographic and hemodynamic effects of coenzyme Q10 in healthy individuals: a double‐blind, randomized controlled trial. Annals of Pharmacotherapy 2007;41(3):420‐5. - PubMed
Shcherbakova 2010 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Shcherbakova AG, Sigitova ON. Assessment of quality of life after inclusion of coenzyme Q10 in the scheme of treatment of women with arterial hypertension and elevated risk of cardiovascular complications. Kardiologiia 2010;50(12):19‐21. - PubMed
Singh 1999 {published data only}
-
- Singh RB, Niaz MA, Rastogi SS, Shukla PK, Thakur AS. Effect of hydrosoluble coenzyme Q10 on blood pressures and insulin resistance in hypertensive patients with coronary artery disease. Journal of Human Hypertension 1999;13:203‐8. - PubMed
Additional references
Burt 1995
-
- Burt VL, Whelton P, Roccella EJ, Brown C, Cutler JA, Higgins M, et al. Prevalence of hypertension in the US adult population. Hypertension. 1995;25(3):303‐4. - PubMed
CHEP 2015
-
- Daskalopoulou SS, Rabi DM, Zarnke K, for the Canadian Hypertension Education Program. The 2015 Canadian Hypertension Education Program recommendations for blood pressure measurement, diagnosis, assessment of risk, prevention, and treatment of hypertension. Canadian Journal of Cardiology 2015; Vol. 31, issue 5:549‐68. - PubMed
Heran 2008a
Heran 2008b
Heran 2012
Langsjoen 1985
Mann 2005
-
- Mann J. The Indo‐Mediterranean diet revisited. Lancet 2005;366:353‐4. - PubMed
McCarty 1999
-
- McCarty MF. Coenzyme Q versus hypertension: does CoQ decrease endothelial superoxide generation?. Medical Hypotheses 1999;53(4):300–4. - PubMed
Musini 2008
Musini 2009a
Musini 2009b
Musini 2014
Niklowitz 2007
O'Brien 2005
-
- O’Brien E, Asmar R, Beilin L, Imai Y, Mancia G, Mengden T, et al. Practice guidelines of the European Society of Hypertension for clinic, ambulatory and self blood pressure measurement. Journal of Hypertension 2005;23:697–701. - PubMed
Pickering 2005
-
- Pickering TG, Hall JE, Appel LJ, Falkner BE, Graves J, Hill MN, et al. Recommendations for blood pressure measurement in humans and experimental animals : Part 1: Blood pressure measurement in humans: A statement for professionals from the subcommittee of professional and public education of the American Heart Association Council on High Blood Pressure Research. Hypertension 2005;45:142‐61. - PubMed
Quinzii 2007
Rosendfeldt 2003
-
- Rosenfeldt F, Hilton D, Pepe S, Krum H. Systematic review of effect of coenzyme Q10 in physical exercise, hypertension and heart failure. BioFactors (Oxford, England) 2003;18:91‐100. - PubMed
Rosenfeldt 2007
-
- Rosenfeldt FL, Haas SJ, Krum H, Hadj A, Ng K, Leong J‐Y, et al. Coenzyme Q10 in the treatment of hypertension: a meta‐analysis of the clinical trials. Journal of Human Hypertension 2007;21:297–306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

