On-site bundled rapid HIV/HCV testing in substance use disorder treatment programs: study protocol for a hybrid design randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 26936623
- PMCID: PMC4776446
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-016-1225-4
On-site bundled rapid HIV/HCV testing in substance use disorder treatment programs: study protocol for a hybrid design randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: More than 1.2 million people in the United States are living with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), and 3.2 million are living with hepatitis C virus (HCV). An estimated 25 % of persons living with HIV also have HCV. It is therefore of great public health importance to ensure the prompt diagnosis of both HIV and HCV in populations that have the highest prevalence of both infections, including individuals with substance use disorders (SUD).
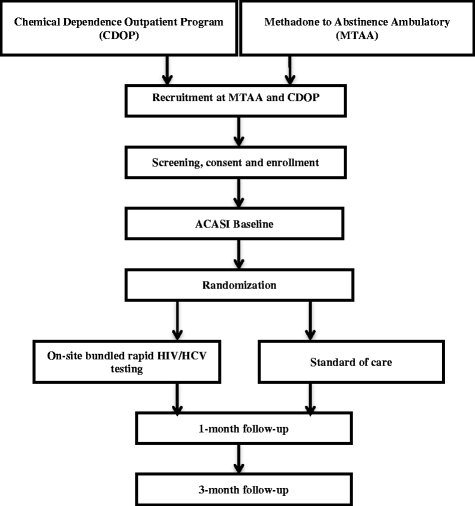
Methods/design: In this theory-driven, efficacy-effectiveness-implementation hybrid study, we will develop and test an on-site bundled rapid HIV/HCV testing intervention for SUD treatment programs. Its aim is to increase the receipt of HIV and HCV test results among SUD treatment patients. Using a rigorous process involving patients, providers, and program managers, we will incorporate rapid HCV testing into evidence-based HIV testing and linkage to care interventions. We will then test, in a randomized controlled trial, the extent to which this bundled rapid HIV/HCV testing approach increases receipt of HIV and HCV test results. Lastly, we will conduct formative research to understand the barriers to, and facilitators of, the adoption, implementation, and sustainability of the bundled rapid testing strategy in SUD treatment programs.
Discussion: Novel approaches that effectively integrate on-site rapid HIV and rapid HCV testing are needed to address both the HIV and HCV epidemics. If feasible and efficacious, bundled rapid HIV/HCV testing may offer a scalable, potentially cost-effective approach to testing high-risk populations, such as patients of SUD treatment programs. It may ultimately lead to improved linkage to care and progress through the HIV and HCV care and treatment cascades.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT02355080 . (30 January 2015).
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: HIV in the united States: At A Glance. http://www.cdc.gov/hiv/statistics/basics/ataglance.html. Accessed 12 June 2015.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: The ABCs of hepatitis. http://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/Resources/Professionals/PDFs/ABCTable.pdf. Accessed 21 October 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical