Proteomic prediction and Renin angiotensin aldosterone system Inhibition prevention Of early diabetic nephRopathy in TYpe 2 diabetic patients with normoalbuminuria (PRIORITY): essential study design and rationale of a randomised clinical multicentre trial
- PMID: 26936907
- PMCID: PMC4785328
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-010310
Proteomic prediction and Renin angiotensin aldosterone system Inhibition prevention Of early diabetic nephRopathy in TYpe 2 diabetic patients with normoalbuminuria (PRIORITY): essential study design and rationale of a randomised clinical multicentre trial
Abstract
Introduction: Diabetes mellitus affects 9% of the European population and accounts for 15% of healthcare expenditure, in particular, due to excess costs related to complications. Clinical trials aiming for earlier prevention of diabetic nephropathy by renin angiotensin system blocking treatment in normoalbumuric patients have given mixed results. This might reflect that the large fraction of normoalbuminuric patients are not at risk of progression, thereby reducing power in previous studies. A specific risk classifier based on urinary proteomics (chronic kidney disease (CKD)273) has been shown to identify normoalbuminuric diabetic patients who later progressed to overt kidney disease, and may hold the potential for selection of high-risk patients for early intervention. Combining the ability of CKD273 to identify patients at highest risk of progression with prescription of preventive aldosterone blockade only to this high-risk population will increase power. We aim to confirm performance of CKD273 in a prospective multicentre clinical trial and test the ability of spironolactone to delay progression of early diabetic nephropathy.
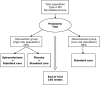
Methods and analysis: Investigator-initiated, prospective multicentre clinical trial, with randomised double-masked placebo-controlled intervention and a prospective observational study. We aim to include 3280 type 2 diabetic participants with normoalbuminuria. The CKD273 classifier will be assessed in all participants. Participants with high-risk pattern are randomised to treatment with spironolactone 25 mg once daily, or placebo, whereas, those with low-risk pattern will be observed without intervention other than standard of care. Treatment or observational period is 3 years.The primary endpoint is development of confirmed microalbuminuria in 2 of 3 first morning voids urine samples.
Ethics and dissemination: The study will be conducted under International Conference on Harmonisation - Good clinical practice (ICH-GCP) requirements, ethical principles of Declaration of Helsinki and national laws. This first new biomarker-directed intervention trial aiming at primary prevention of diabetic nephropathy may pave the way for personalised medicine approaches in treatment of diabetes complications.
Trial registration number: NCT02040441; Pre-results.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical