Combined effects of alpha particles and depleted uranium on Zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos
- PMID: 26937024
- PMCID: PMC4973638
- DOI: 10.1093/jrr/rrv104
Combined effects of alpha particles and depleted uranium on Zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos
Abstract
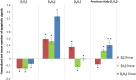
The combined effects of low-dose or high-dose alpha particles and depleted uranium (DU) in Zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos were studied. Three schemes were examined-(i) [ILUL]: 0.44 mGy alpha-particle dose + 10 µg/l DU exposure, (ii) [IHUH]: 4.4 mGy alpha-particle dose + 100 µg/l DU exposure and (iii) [IHUL]: 4.4 mGy alpha-particle dose + 10 µg/l DU exposure-in which Zebrafish embryos were irradiated with alpha particles at 5 h post fertilization (hpf) and/or exposed to uranium at 5-6 hpf. The results were also compared with our previous work, which studied the effects of [ILUH]: 0.44 mGy alpha-particle dose + 100 µg/l DU exposure. When the Zebrafish embryos developed to 24 hpf, the apoptotic signals in the entire embryos, used as the biological endpoint for this study, were quantified. Our results showed that [ILUL] and [IHUL] led to antagonistic effects, whereas [IHUH] led to an additive effect. The effect found for the previously studied case of [ILUH] was difficult to define because it was synergistic with reference to the 100 µg/l DU exposure, but it was antagonistic with reference to the 0.44 mGy alpha-particle dose. All the findings regarding the four different schemes showed that the combined effects critically depended on the dose response to each individual stressor. We also qualitatively explained these findings in terms of promotion of early death of cells predisposed to spontaneous transformation by alpha particles, interacting with the delay in cell death resulting from various concentrations of DU exposure.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Japan Radiation Research Society and Japanese Society for Radiation Oncology.
Figures



References
-
- Salbu B, Rosseland BO, Oughton DH. Multiple stressors; a challenge for the future. J Environ Monit 2005;7:539. - PubMed
-
- Salbu B, Mothersill C, Denbeigh J et al. . Environmentally relevant mixed exposures to radiation and heavy metals induce measurable stress responses in Atlantic salmon. Env Sci Technol 2008;42:3441–6. - PubMed
-
- Mothersill C, Salbu B, Heier LS et al. . Multiple stressor effects of radiation and metals in salmon (Salmo salar). J Environ Radioact 2007;96:20–31. - PubMed
-
- Mothersill C, Smith RW, Heier LS et al. . Radiation-induced bystander effects in the Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) following mixed exposure to copper and aluminum combined with low-dose gamma radiation. Radiat Environ Biophys 2014;53:103–14. - PubMed
-
- Olsvik PA, Heier LS, Rosseland BO et al. . Effects of combined γ-irradiation and metal (Al + Cd) exposures in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar). J Environ Radioact 2010;101:230–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

