Novel Role for Protein Inhibitor of Activated STAT 4 (PIAS4) in the Restriction of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 by the Cellular Intrinsic Antiviral Immune Response
- PMID: 26937035
- PMCID: PMC4836348
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.03055-15
Novel Role for Protein Inhibitor of Activated STAT 4 (PIAS4) in the Restriction of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 by the Cellular Intrinsic Antiviral Immune Response
Abstract
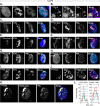
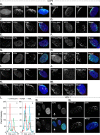
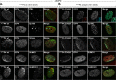
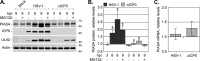
Small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) is used by the intrinsic antiviral immune response to restrict viral pathogens, such as herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1). Despite characterization of the host factors that rely on SUMOylation to exert their antiviral effects, the enzymes that mediate these SUMOylation events remain to be defined. We show that unconjugated SUMO levels are largely maintained throughout infection regardless of the presence of ICP0, the HSV-1 SUMO-targeted ubiquitin ligase. Moreover, in the absence of ICP0, high-molecular-weight SUMO-conjugated proteins do not accumulate if HSV-1 DNA does not replicate. These data highlight the continued importance for SUMO signaling throughout infection. We show that the SUMO ligase protein inhibitor of activated STAT 4 (PIAS4) is upregulated during HSV-1 infection and localizes to nuclear domains that contain viral DNA. PIAS4 is recruited to sites associated with HSV-1 genome entry through SUMO interaction motif (SIM)-dependent mechanisms that are destabilized by ICP0. In contrast, PIAS4 accumulates in replication compartments through SIM-independent mechanisms irrespective of ICP0 expression. Depletion of PIAS4 enhances the replication of ICP0-null mutant HSV-1, which is susceptible to restriction by the intrinsic antiviral immune response. The mechanisms of PIAS4-mediated restriction are synergistic with the restriction mechanisms of a characterized intrinsic antiviral factor, promyelocytic leukemia protein, and are antagonized by ICP0. We provide the first evidence that PIAS4 is an intrinsic antiviral factor. This novel role for PIAS4 in intrinsic antiviral immunity contrasts with the known roles of PIAS proteins as suppressors of innate immunity.
Importance: Posttranslational modifications with small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) proteins regulate multiple aspects of host immunity and viral replication. The protein inhibitor of activated STAT (PIAS) family of SUMO ligases is predominantly associated with the suppression of innate immune signaling. We now identify a unique and contrasting role for PIAS proteins as positive regulators of the intrinsic antiviral immune response to herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) infection. We show that PIAS4 relocalizes to nuclear domains that contain viral DNA throughout infection. Depletion of PIAS4, either alone or in combination with the intrinsic antiviral factor promyelocytic leukemia protein, significantly impairs the intrinsic antiviral immune response to HSV-1 infection. Our data reveal a novel and dynamic role for PIAS4 in the cellular-mediated restriction of herpesviruses and establish a new functional role for the PIAS family of SUMO ligases in the intrinsic antiviral immune response to DNA virus infection.
Copyright © 2016 Conn et al.
Figures

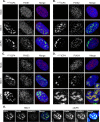
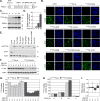
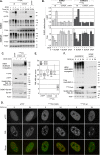
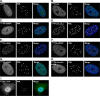

Similar articles
-
SUMO Ligase Protein Inhibitor of Activated STAT1 (PIAS1) Is a Constituent Promyelocytic Leukemia Nuclear Body Protein That Contributes to the Intrinsic Antiviral Immune Response to Herpes Simplex Virus 1.J Virol. 2016 Jun 10;90(13):5939-5952. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00426-16. Print 2016 Jul 1. J Virol. 2016. PMID: 27099310 Free PMC article.
-
Sequences related to SUMO interaction motifs in herpes simplex virus 1 protein ICP0 act cooperatively to stimulate virus infection.J Virol. 2014 Mar;88(5):2763-74. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03417-13. Epub 2013 Dec 18. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24352468 Free PMC article.
-
SUMO pathway dependent recruitment of cellular repressors to herpes simplex virus type 1 genomes.PLoS Pathog. 2011 Jul;7(7):e1002123. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002123. Epub 2011 Jul 14. PLoS Pathog. 2011. PMID: 21779164 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of alphaherpesvirus infections by the ICP0 family of proteins.J Gen Virol. 2013 Mar;94(Pt 3):465-481. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.048900-0. Epub 2012 Dec 12. J Gen Virol. 2013. PMID: 23239572 Review.
-
The use of fluorescence microscopy to study the association between herpesviruses and intrinsic resistance factors.Viruses. 2011 Dec;3(12):2412-24. doi: 10.3390/v3122412. Epub 2011 Dec 7. Viruses. 2011. PMID: 22355446 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Viral manipulation of the cellular sumoylation machinery.Cell Commun Signal. 2017 Jul 14;15(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12964-017-0183-0. Cell Commun Signal. 2017. PMID: 28705221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct temporal roles for the promyelocytic leukaemia (PML) protein in the sequential regulation of intracellular host immunity to HSV-1 infection.PLoS Pathog. 2018 Jan 8;14(1):e1006769. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006769. eCollection 2018 Jan. PLoS Pathog. 2018. PMID: 29309427 Free PMC article.
-
Duck PIAS2 Promotes H5N1 Avian Influenza Virus Replication Through Its SUMO E3 Ligase Activity.Front Microbiol. 2020 Jun 11;11:1246. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01246. eCollection 2020. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32595623 Free PMC article.
-
"Non-Essential" Proteins of HSV-1 with Essential Roles In Vivo: A Comprehensive Review.Viruses. 2020 Dec 23;13(1):17. doi: 10.3390/v13010017. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 33374862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Daxx mediated histone H3.3 deposition on HSV-1 DNA restricts genome decompaction and the progression of immediate-early transcription.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 15:2024.08.15.608064. doi: 10.1101/2024.08.15.608064. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: PLoS Pathog. 2025 Aug 20;21(8):e1012501. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1012501. PMID: 39185184 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Arvin A, Campadelli-Fiume G, Mocarski E, Moore PS, Roizman B, Whitley R, Yamanishi K. 2007. Human herpesviruses: biology, therapy, and immunoprophylaxis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

