MicroRNA-19b-3p Modulates Japanese Encephalitis Virus-Mediated Inflammation via Targeting RNF11
- PMID: 26937036
- PMCID: PMC4836334
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02586-15
MicroRNA-19b-3p Modulates Japanese Encephalitis Virus-Mediated Inflammation via Targeting RNF11
Abstract
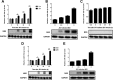
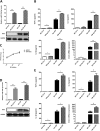
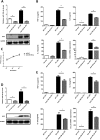
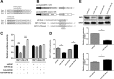
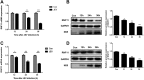
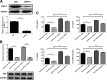
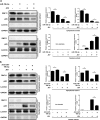
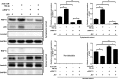
Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) can invade the central nervous system and consequently induce neuroinflammation, which is characterized by profound neuronal cell damage accompanied by astrogliosis and microgliosis. Albeit microRNAs (miRNAs) have emerged as major regulatory noncoding RNAs with profound effects on inflammatory response, it is unknown how astrocytic miRNAs regulate JEV-induced inflammation. Here, we found the involvement of miR-19b-3p in regulating the JEV-induced inflammatory responsein vitroandin vivo The data demonstrated that miR-19b-3p is upregulated in cultured cells and mouse brain tissues during JEV infection. Overexpression of miR-19b-3p led to increased production of inflammatory cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor alpha, interleukin-6, interleukin-1β, and chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5, after JEV infection, whereas knockdown of miR-19b-3p had completely opposite effects. Mechanistically, miR-19b-3p modulated the JEV-induced inflammatory response via targeting ring finger protein 11, a negative regulator of nuclear factor kappa B signaling. We also found that inhibition of ring finger protein 11 by miR-19b-3p resulted in accumulation of nuclear factor kappa B in the nucleus, which in turn led to higher production of inflammatory cytokines.In vivosilencing of miR-19b-3p by a specific antagomir reinvigorates the expression level of RNF11, which in turn reduces the production of inflammatory cytokines, abrogates gliosis and neuronal cell death, and eventually improves the survival rate in the mouse model. Collectively, our results demonstrate that miR-19b-3p positively regulates the JEV-induced inflammatory response. Thus, miR-19b-3p targeting may constitute a thought-provoking approach to rein in JEV-induced inflammation.
Importance: Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) is one of the major causes of acute encephalitis in humans worldwide. The pathological features of JEV-induced encephalitis are inflammatory reactions and neurological diseases resulting from glia activation. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small noncoding RNAs that regulate gene expression posttranscriptionally. Accumulating data indicate that miRNAs regulate a variety of cellular processes, including the host inflammatory response under pathological conditions. Recently, a few studies demonstrated the role of miRNAs in a JEV-induced inflammatory response in microglia; however, their role in an astrocyte-derived inflammatory response is largely unknown. The present study reveals that miR-19b-3p targets ring finger protein 11 in glia and promotes inflammatory cytokine production by enhancing nuclear factor kappa B activity in these cells. Moreover, administration of an miR-19b-3p-specific antagomir in JEV-infected mice reduces neuroinflammation and lethality. These findings suggest a new insight into the molecular mechanism of the JEV-induced inflammatory response and provide a possible therapeutic entry point for treating viral encephalitis.
Copyright © 2016 Ashraf et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-15b Modulates Japanese Encephalitis Virus-Mediated Inflammation via Targeting RNF125.J Immunol. 2015 Sep 1;195(5):2251-62. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1500370. Epub 2015 Jul 22. J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26202983
-
MicroRNA 155 regulates Japanese encephalitis virus-induced inflammatory response by targeting Src homology 2-containing inositol phosphatase 1.J Virol. 2014 May;88(9):4798-810. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02979-13. Epub 2014 Feb 12. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24522920 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA JINR1 regulates miR-216b-5p/GRP78 and miR-1-3p/DDX5 axis to promote JEV infection and cell death.J Virol. 2025 May 20;99(5):e0006625. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00066-25. Epub 2025 Apr 24. J Virol. 2025. PMID: 40272157 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenicity and virulence of Japanese encephalitis virus: Neuroinflammation and neuronal cell damage.Virulence. 2021 Dec;12(1):968-980. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2021.1899674. Virulence. 2021. PMID: 33724154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of miRNA Regulation in Japanese Encephalitis (JEV) Virus Infection.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024;25(5):521-533. doi: 10.2174/0113892010241606231003102047. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 37888811 Review.
Cited by
-
Exosomes from osteoarthritic fibroblast-like synoviocytes promote cartilage ferroptosis and damage via delivering microRNA-19b-3p to target SLC7A11 in osteoarthritis.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 24;14:1181156. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1181156. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37691947 Free PMC article.
-
The Efficacy of Cardiac Anti-miR-208a Therapy Is Stress Dependent.Mol Ther. 2017 Mar 1;25(3):694-704. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2017.01.012. Epub 2017 Feb 12. Mol Ther. 2017. PMID: 28202391 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal miR-19b-3p communicates tubular epithelial cells and M1 macrophage.Cell Death Dis. 2019 Oct 10;10(10):762. doi: 10.1038/s41419-019-2008-0. Cell Death Dis. 2019. PMID: 31601790 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
MicroRNA-22 negatively regulates poly(I:C)-triggered type I interferon and inflammatory cytokine production via targeting mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein (MAVS).Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 22;7(47):76667-76683. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12395. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27705941 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma microRNAs as a Potential Biomarker for Identification of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 May 11;12(5):1204. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12051204. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35626359 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

