Hydraulic fracturing water use variability in the United States and potential environmental implications
- PMID: 26937056
- PMCID: PMC4758395
- DOI: 10.1002/2015WR017278
Hydraulic fracturing water use variability in the United States and potential environmental implications
Abstract
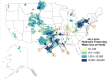
A U.S. map of water volumes used to hydraulically fracture oil and gas wells, 2011-2014Hydraulic fracturing water volumes differ regionally across the U.S.Discussion of variation in water use and potential environmental implications.
Keywords: hydraulic fracturing; shale gas; unconventional oil and gas; water use; well stimulation.
Figures


Comment in
-
UK regulations: Could fracking creep under the radar?Nature. 2017 Aug 23;548(7668):393. doi: 10.1038/548393a. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28836601 No abstract available.
References
-
- Brittingham, M. C. , Maloney K. O., Farag A. M., Harper D. D., and Bowen Z. H. (2014), Ecological risks of shale oil and gas development to wildlife, aquatic resources and their habitats, Environ. Sci. Technol., 48(19), 11,034–11,047. - PubMed
-
- Clark, C. E. , Horner R. M., and Harto C. B. (2013), Life cycle water consumption for shale gas and conventional natural gas, Environ. Sci. Technol., 47(20), 11,829–11,836. - PubMed
-
- Elbel, J. , and Britt L. (2000), Fracture treatment design, in Reservoir Stimulation, edited by Economides M. J. and Nolte K. G., John Wiley, West Sussex, England.
-
- Gallegos, T. J. , and Varela B. A. (2015a), Trends in hydraulic fracturing distributions and treatment fluids, additives, proppants, and water volumes applied to wells drilled in the United States from 1947 through 2010—Data analysis and comparison to the literature, U.S. Geol. Surv. Sci. Invest. Rep. 2014–5131, 15 pp., U.S. Geol. Surv., Reston, Va. [Available at http://dx.doi.org/10.3133/sir20145131.] - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
